IL23 signaling pathway IL23 plays important role in expanding and maintaining the Th17 cell population, a novel Tcell subset involved in antimicrobial immune response and establishment of many autoimmune diseases 1 IL23 receptor is composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R IL23R associates with JAK2 and in a liganddependent manner with STAT3 2The role of the IL23/Th17 pathway in cardiometabolic comorbidity associated with psoriasis Egeberg A(1), Gisondi P(2), Carrascosa JM(3), Warren RB(4), Mrowietz U(5) Author information (1)Gentofte Hospital, Department of Dermatology and Allergy Hellerup, Denmark (2)Section of Dermatology and Venereology, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyTogether, these findings demonstrate an important role for the IL23IL17 immune pathway in host defense against P carinii during infection Infection models using IL12p40−/− and IL12p35−/− mice have shown that there is an IL12p40dependent,
2
Il-23 pathway psoriasis
Il-23 pathway psoriasis-The cytokines IL23 and IL17 have an important role in the pathogenesis of, and as a therapeutic target in, both animal models of chronic inflammation and some human chronic inflammatory diseases The traditional view is that a main source of IL17 is T cells and that IL17 production is under the control of IL23 IL17 inhibition has shown good efficacy in clinical trials for ankylosingTREMFYA® (guselkumab) Study Indicating The Significance Of Inhibiting IL23 Pathway In Adults With Psoriatic Arthritis Published In The Lancet


Www Jci Org Articles View Version 1 Pdf Render Pdf
Both IL12 and IL23 bind to the b1 receptor of T cells and natural killer cells via their shared p40 subunit 1,7 This new class of drugs has been designed to function by binding with high affinity to the p40 subunit, thus preventing its binding at the receptor and the subsequent downstream signalingBoth IL12 and IL23 bind to the b1 receptor of T cells and natural killer cells via their shared p40 subunit 1,7 This new class of drugs has been designed to function by binding with high affinity to the p40 subunit, thus preventing its binding at the receptor and the subsequent downstream signalingClinical trials and reallife studies have demonstrated that drugs targeting the p19 or p40 subunit of IL23 are promising in the treatment of patients with enthesitis The use of inhibitors which target the IL23 pathway could represent a valid treatment option for PsArelated enthesitis This box summarizes key points contained in the article
OBJECTIVE The interleukin (IL)23 pathway contributes to IBD pathogenesis and is being actively studied as a therapeutic target in patients with IBD Unexpected outcomes in these therapeutic trials have highlighted the importance of understanding the cell types and mechanisms through which IL23 regulates immune outcomes How IL23 regulates macrophage outcomes and the consequences of the IL23RIL12, IL23 and Type I IFNs, which are critical in driving the function of Th1 cells, Th17 cells and the innate immune response8,9 Immune Cell Immune Cell Immune Cell Release of cytokines Activation of downstream signaling molecules STAT activation and relocation into the nucleus Promotes expression of e˙ector molecules Cytokines can furtherSeveral lines of evidence support a critical role of the IL23–IL17 pathway in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) First, the loss of function of IL23R R381Q gene mutation is associated with protection from AS because of impaired IL17A production Conversely, IL23R variants and other ASassociated genes with known effects on the IL23 pathway are also identified to be strongly associated with
The IL23 pathway has emerged as a promising target in the management of psoriatic diseases This LIVE clinical dialogue aims to give a timely update on the newest developments from both dermatological and rheumatological perspectivesIL23 signaling pathway IL23 plays important role in expanding and maintaining the Th17 cell population, a novel Tcell subset involved in antimicrobial immune response and establishment of many autoimmune diseases IL23 receptor is composed of IL12RB1 and IL23R IL23R associates with JAK2 and in a liganddependent manner with STAT3The themes addressed by this Research Topic will include, but are not limited to, the followings • IL17 producing cell subsets in health and disease, with a focus on SpA, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) • The IL23/IL17 pathway and microbiota in the pathogenesis of CID • Human monogenic mutations and



Interleukin 12 Biological Properties And Clinical Application Clinical Cancer Research



Discovery Of The Il 23 Il 17 Signaling Pathway And The Treatment Of Psoriasis The Journal Of Immunology
The interleukin 12 (IL12)/IL23 common pathway has been found to play a determinant role in the induction of inflammation in adaptive immune responsesInterleukin23 (IL23) is known to play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of T helper 17 cells It has been previously demonstrated that IL17 is involved in experimental Lyme arthritis, caused by Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria However, the precise role of the IL23 receptor (IL23R) for the B burgdorferiinduced IL17 responses or human Lyme disease has not yet been elucidatedInterleukin23 (IL23) is a heterodimeric cytokine composed of an IL12B (IL12p40) subunit (that is shared with IL12) and the IL23A (IL23p19) subunit IL23 is part of IL12 family of cytokines A functional receptor for IL23 (the IL23 receptor) has been identified and is composed of IL12R β1 and IL23R
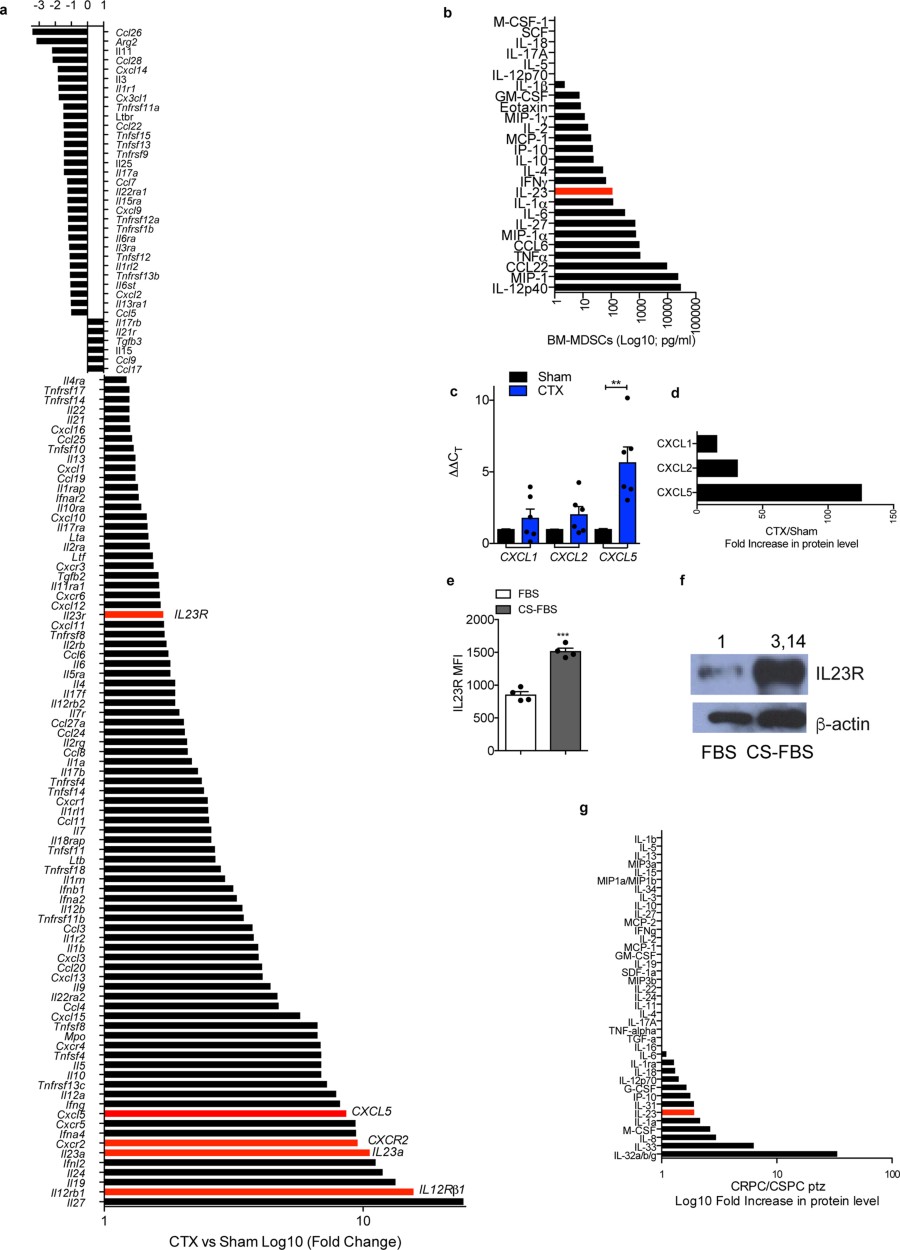


Extended Data Fig 5 Il 23 Pathway Is The Most Upregulated In The Tumour After Castration Nature



Targeting The Th17 Pathway Helper T Th 17 Cells Are Derived From Download Scientific Diagram
The IL23/IL17 axis is an important pathway for targeted therapy for inflammatory diseases Emerging evidence from clinical trials has shown that monoclonal antibodies against IL23, IL17, and tumor necrosis factor are effective in the treatment of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, pityriasis rubra pilarisThe Interleukin 23 (IL23) cytokine is a heterodimeric cytokine consisting of the two subunits p19 and p40 It is an inducer of the Th17 cell population and a component of the IL23/IL17 immune pathway which is an orchestrator of many pathological conditions, including psoriasis1750–15 Clinical dialogue IL23 pathway in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis – interactive panel discussion Alexander Egeberg and Kilian Eyerich, moderated by Chris Griffiths 15–10 Conclusion and close Chris Griffiths More Info 1 Hours Faculty Alexander Egeberg


Www Gastrojournal Org Article S0016 5085 16 9 Pdf


Http Eprints Whiterose Ac Uk 1 Combo Biologics Psa Manuscript Letter V12 Apr18clean Pdf
The activation of IL23dependent and independent pathway by lactic acid (A) The effect of antiIL23 antibodies on the increased production of IL17A in total OTII splenocytes (left) or the coculture of CD11b and OTII CD4 T cells (right) In the presence of antiIL23p19 (αp19) or control antibodies (Cont), cells were stimulatedInterleukin23 (IL23) is known to play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of T helper 17 cells It has been previously demonstrated that IL17 is involved in experimental Lyme arthritis, caused by Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria However, the precise role of the IL23 receptor (IL23R) for the B burgdorferiinduced IL17 responses or human Lyme disease has not yet been elucidatedOBJECTIVE The interleukin (IL)23 pathway contributes to IBD pathogenesis and is being actively studied as a therapeutic target in patients with IBD Unexpected outcomes in these therapeutic trials have highlighted the importance of understanding the cell types and mechanisms through which IL23 regulates immune outcomes How IL23 regulates macrophage outcomes and the consequences of the IL23R
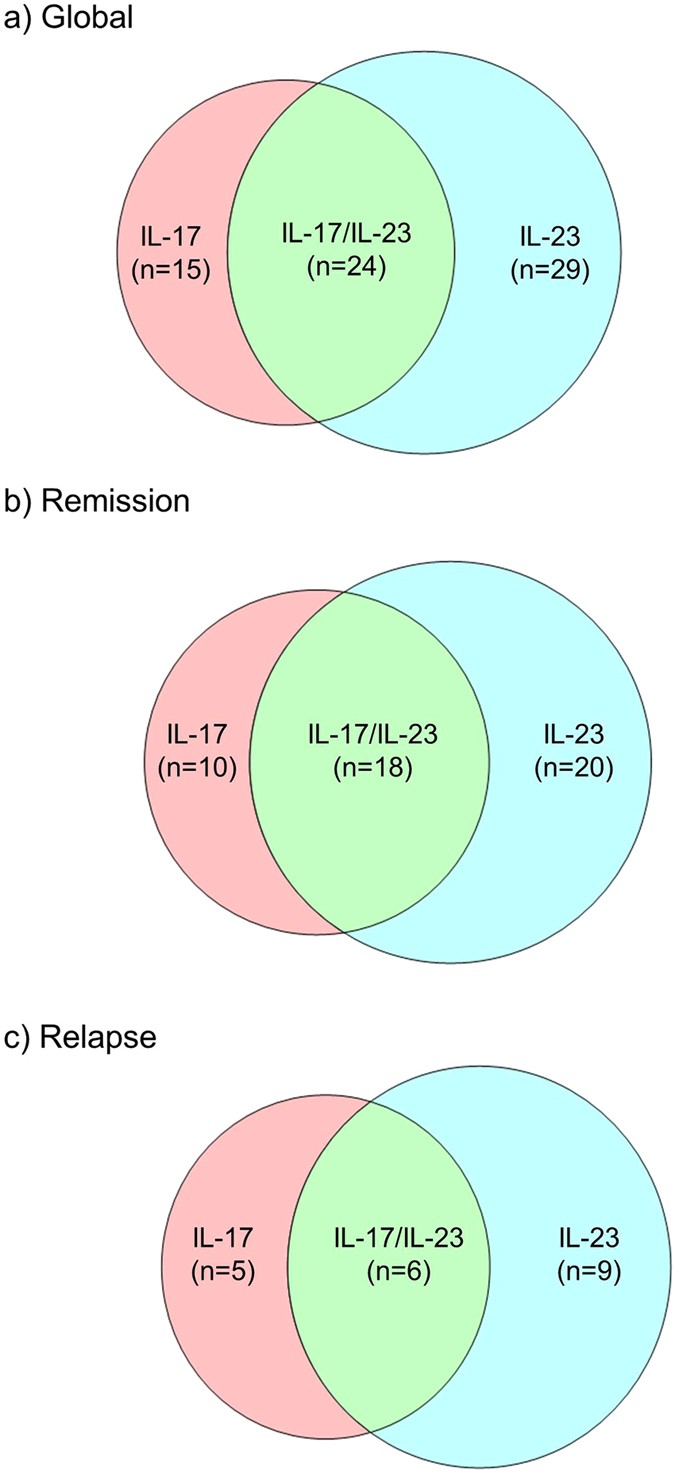


Integrating Longitudinal Serum Il 17 And Il 23 Follow Up Along With Autoantibodies Variation Contributes To Predict Bullous Pemphigoid Outcome Scientific Reports
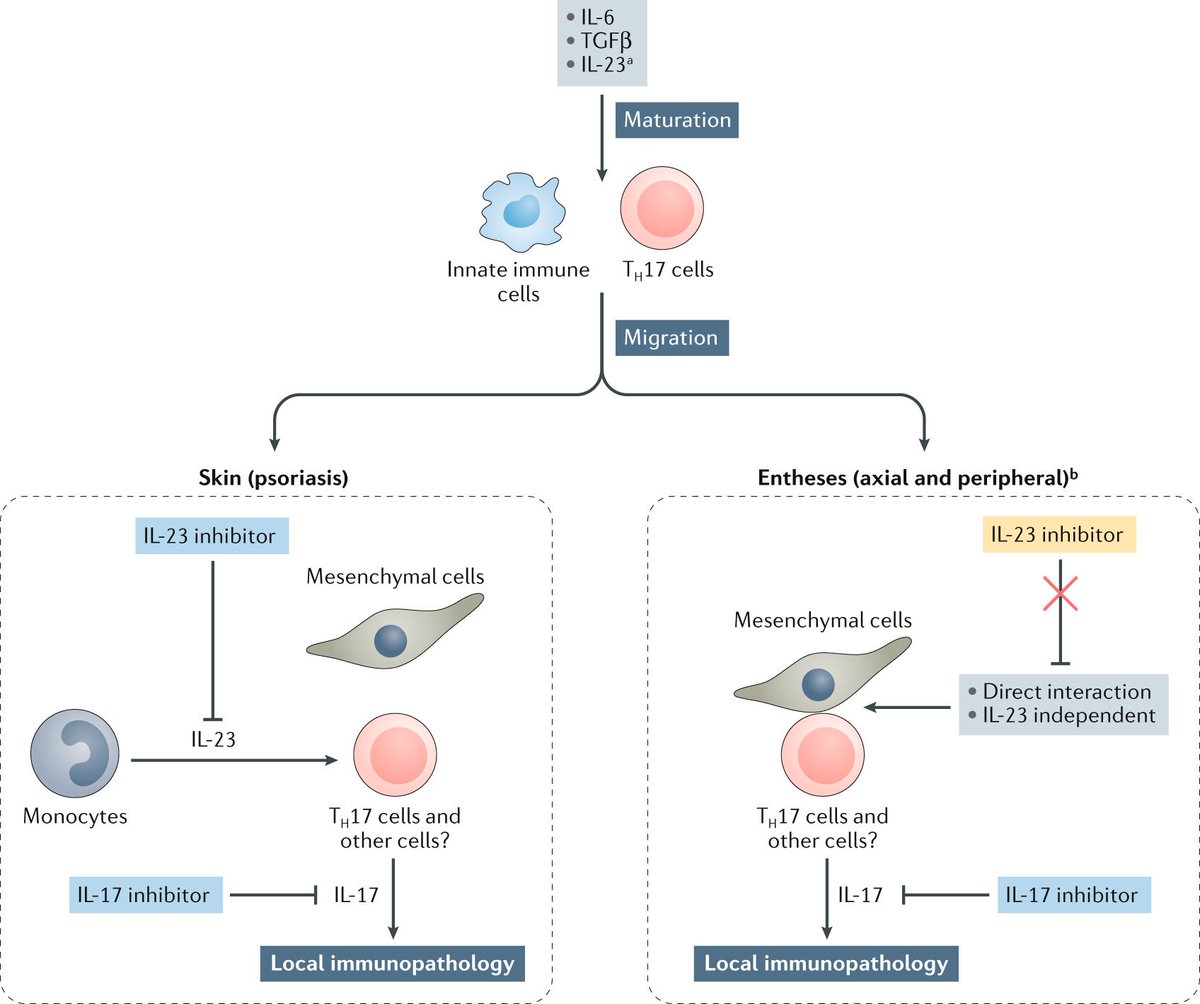


Natrevrheumatol Decemberissue Therapies Targeting Il 23 Have Failed In Clinical Trials In Axial Spondyloarthritis Axspa Despite The Importance Of The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway In Axspa Pathogenesis Find Out Why In Our
If the IL23–IL17 immune pathway becomes dysregulated, there is a danger of breaking tolerance to 'self' tissues and antigens, leading to severe autoimmune pathologies such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis and Crohn's disease, which severely debilitate millions of sufferersIL23 can activate similar signaling pathways as does IL12, although IL23 induces weak activation of STAT4 Rather, IL23 is a potent activator of the STAT3 transcription factor IL23 is produced by numerous cell types including activated macrophages and DCsThe discovery of the Th17/IL23 pathway adds to the complexity of psoriasis pathogenesis and provides targets for new drug development Not only are there upstream IL23 p19 and IL23 receptor neutralizing drugs in development, there are currently also downstream IL17 antagonists in trials as well



Interleukin 21 Signaling Functions In Cancer And Autoimmunity Clinical Cancer Research


Www Ijbs Com V08p1254 Pdf
IL23 is a potent stimulus for Th17 cells These cells have a distinct developmental pathway from Th1 cells induced by IL12 and are implicated in autoimmune and inflammatory disorders including multiple sclerosis (MS) TGFβ, IL6, and IL1, the transcriptional regulator RORγt (RORC) and IL23 are implicated in Th17 development and maintenanceProtagonist Therapeutics Announces First Subject Dosed in Phase 1 Study of Oral IL23 Receptor Antagonist PN235 (JNJ) December 16, , 730 AM ESTNew promising treatments have been developed for psoriasis that target different parts of the interleukin (IL)23/IL17 pathway This approach is believed to be more disease specific, and sparing the T helper 1 pathway might prevent serious longterm adverse events Moreover, superior Psoriasis Area and Severity Index improvements are observed, which has redefined treatment goals in psoriasis
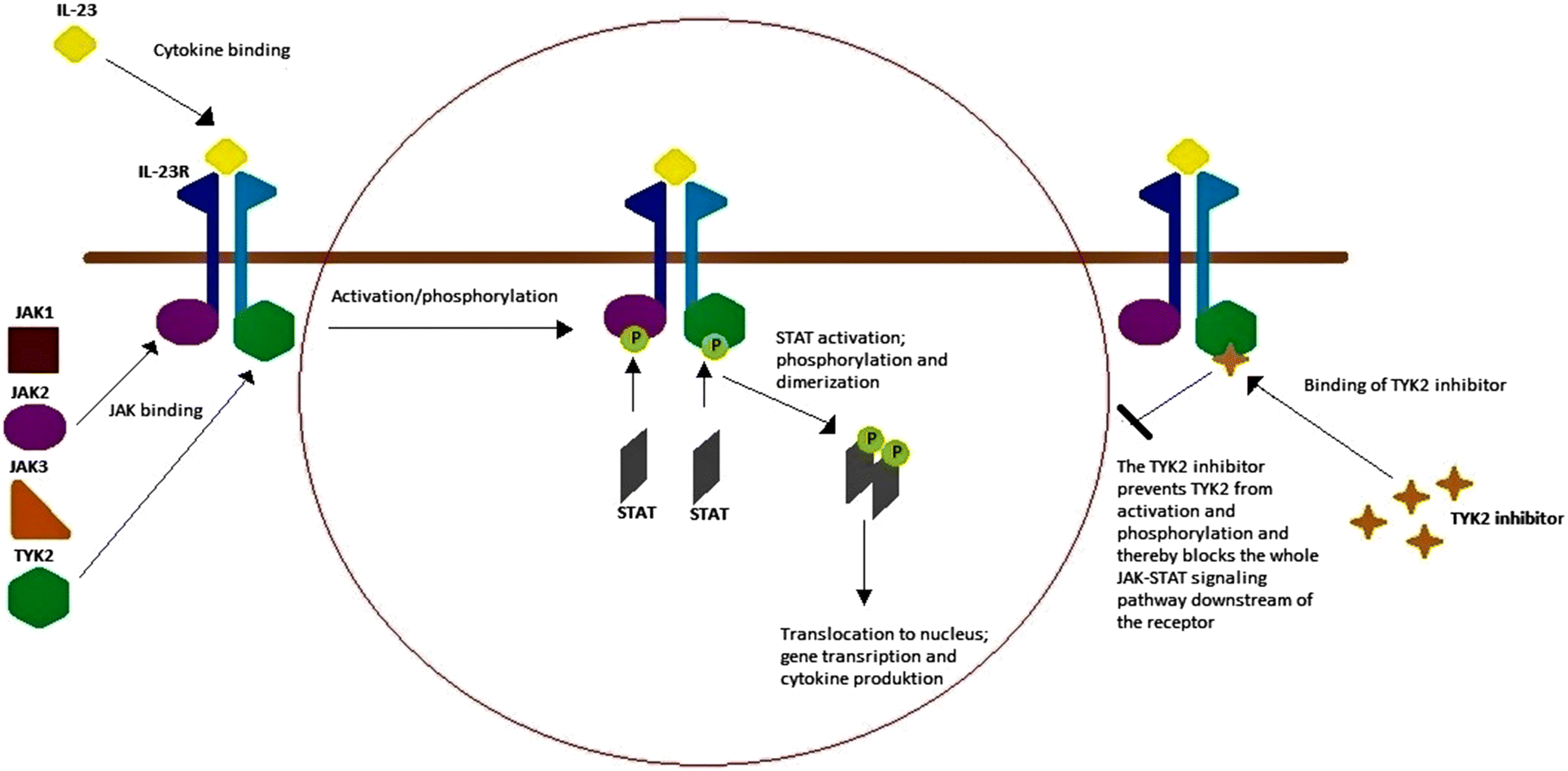


Figure 1 Systemic Treatment Of Psoriasis With Jak Inhibitors A Review Springerlink


2
For this, we calculated a STATpathway specific wGRS for each of the IL6/STAT3, IL12/STAT4 and IL23/STAT3pathways This analysis showed no significant correlation between the coincidence of MSrisk alleles in either of the IL6/STAT3, IL12/STAT4, or IL23/STAT3pathways and the activity of the pathwayInterleukin23 (IL23) is a heterodimer of Interleukin12 subunit beta (IL12B, IL12p40), which is shared with IL12, and Interleukin23 subunit alpha IL23A (IL23p19) subunitPhosphoproteomics of interleukin17secreting T cells (Th17 cells) identifies more than 100 phosphorylation events in response to interleukin23 stimulation, revealing increased phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chain (RLC) and a role for an IL23/ROCK pathway in controlling migration of Th17 and Tγδ17 cells


D Nb Info 34


Www Cell Com Immunity Pdf S1074 7613 18 6 Pdf
Prof Reich discussed the role of the IL23 pathway in psoriatic skin inflammation, highlighting how IL23 inhibition results in high levels of clinical response in the majority of treated patients with psoriasis and the importance of early treatment for maximal disease modification Studies are currently ongoingIn contrast, IL23 signaling is involved in the stabilization and maintenance of Th17 cells, promotes memory T cell activation, and stimulates IL17mediated neutrophil recruitment to sites of infection Although these activities demonstrate that IL12 and IL23 induce different immune responses, both can be characterized as proinflammatoryThat's to say, high serum IL23 level and its active JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway play a critical role in resulting in high serum IL17 level and high frequency of Th17 existed in active AS patients In this way, our results suggest the possible role of JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway and IL23/Th17 axis in pathogenesis of AS



Effects Of The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway On Bone In Spondyloarthritis Semantic Scholar
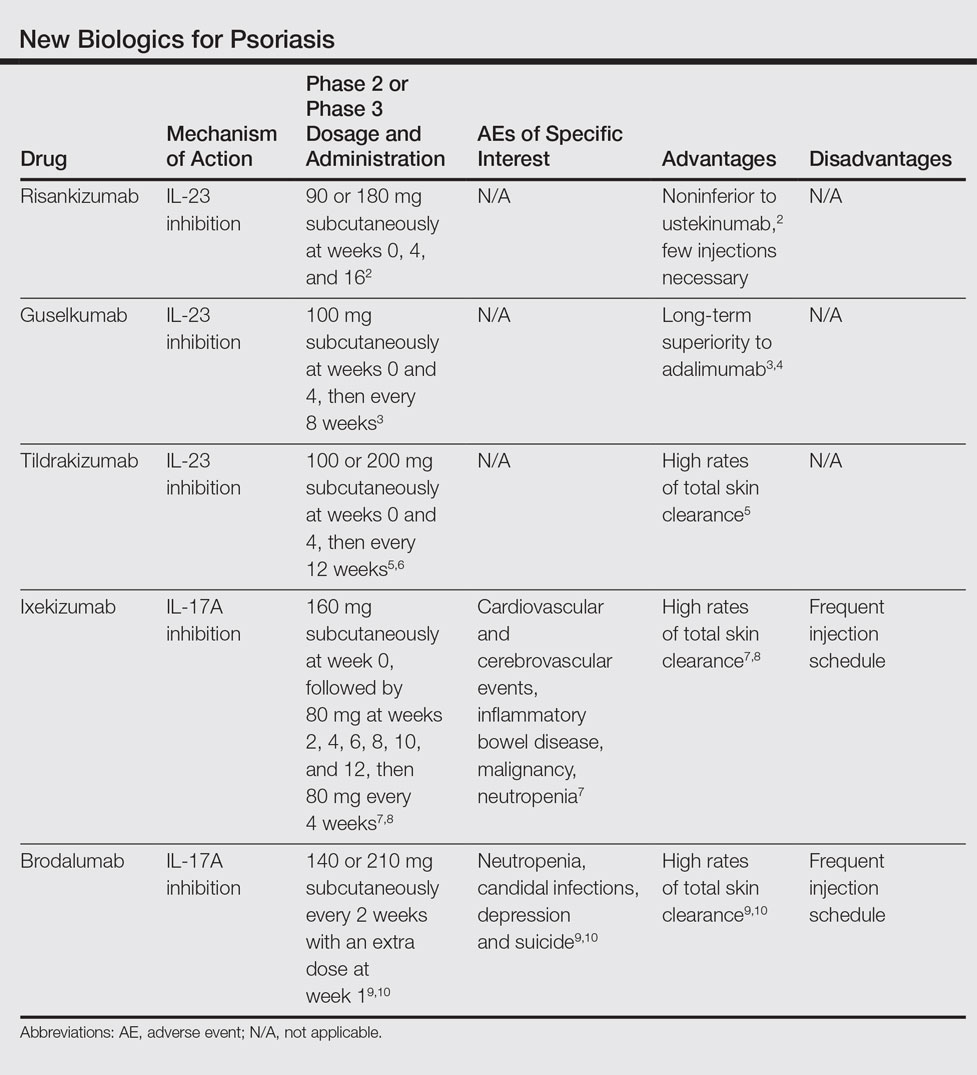


New Biologics In Psoriasis An Update On Il 23 And Il 17 Inhibitors Mdedge Dermatology
Maui, Hawaii Disclosure Mahadevan reports consulting for AbbVie, Janssen, Pfizer and Takeda andThe study, "Il23/Th17 cell pathway A promising target to alleviate thymic inflammation maintenance in myasthenia gravis," was published in the Journal of Autoimmunity Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disorder caused by the abnormal production of antibodies against acetylcholine receptors (AChR) that are necessary for muscleIL12 Signaling Pathway Background Interleukin 12 (IL12) family is unique in having the only heterodimeric cytokines, including IL12, IL23, IL27 and IL35 The heterodimeric cytokines of the IL12 family consist of an αchain (p19, p28 or p35) and a βchain (p40 or Ebi3) The αchains have a fourhelix bundle structure characteristic of


Www Tandfonline Com Doi Pdf 10 1080 18


2
Blockade of IL‐23 pathway with either anti‐p40 or anti‐p19 subunits has resulted in some spectacular therapeutic successes in psoriasis and PsA including improvement in enthesitis in the peripheral skeleton but has failed to demonstrate efficacy in AS that is largely a spinal polyenthesitisNew promising treatments have been developed for psoriasis that target different parts of the interleukin (IL)23/IL17 pathway This approach is believed to be more disease specific, and sparing the T helper 1 pathway might prevent serious longterm adverse events Moreover, superior Psoriasis Area and Severity Index improvements are observed, which has redefined treatment goals in psoriasisBlockade of IL‐23 pathway with either anti‐p40 or anti‐p19 subunits has resulted in some spectacular therapeutic successes in psoriasis and PsA including improvement in enthesitis in the peripheral skeleton but has failed to demonstrate efficacy in AS that is largely a spinal polyenthesitis


Digitalcommons Wustl Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 6660 Context Open Access Pubs
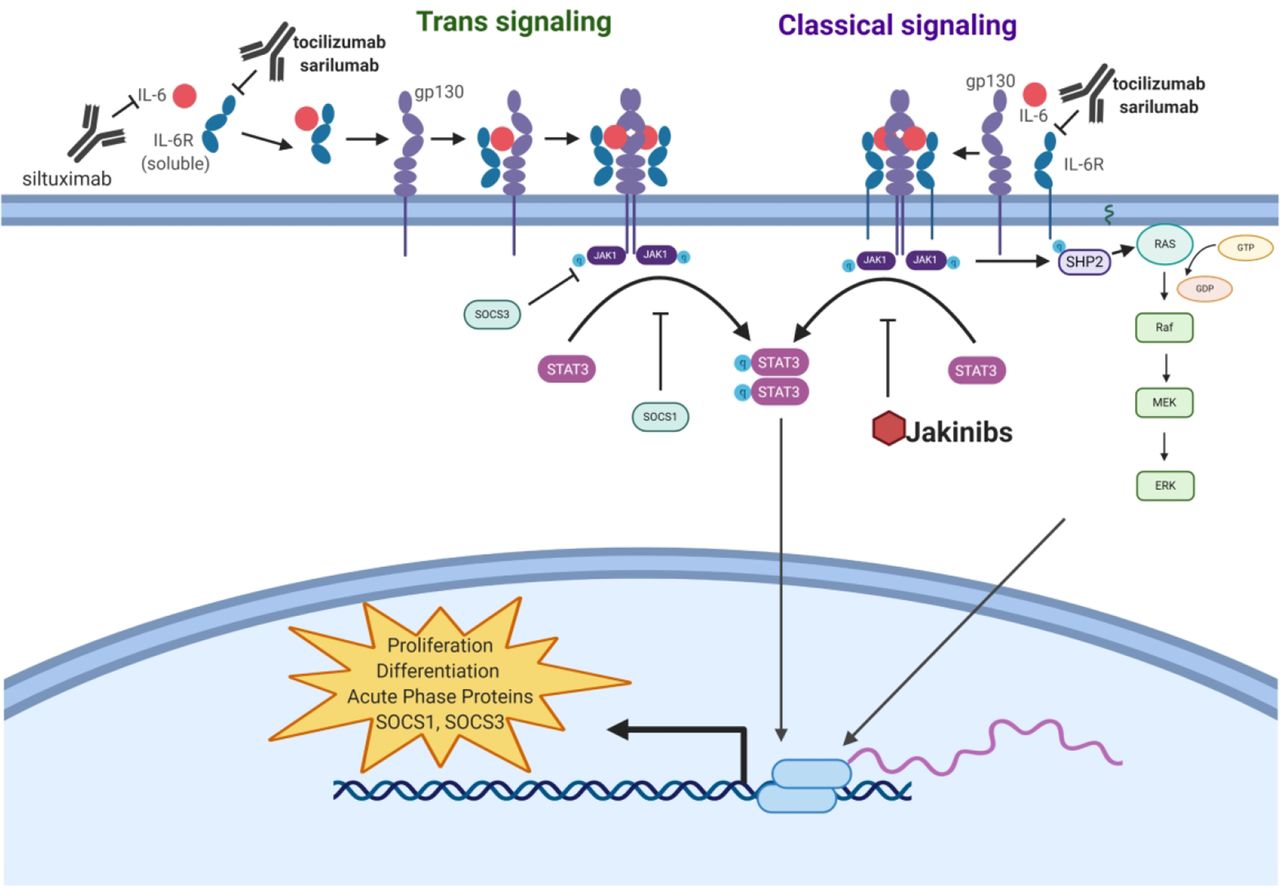


The Society For Immunotherapy Of Cancer Perspective On Regulation Of Interleukin 6 Signaling In Covid 19 Related Systemic Inflammatory Response Journal For Immunotherapy Of Cancer
Pathway network for Immune response IL23 signaling pathway SuperPath 8 Pathways in the Immune response IL23 signaling pathway SuperPath Development Angiopoietin Tie2 signaling IL23mediated signaling events Immune response IL10 signaling pathway Development PDGF signaling via STATs and NFkBBiology of the IL23 pathway beyond the skin Over the past few years, the IL23 pathway has emerged as a promising target for therapeutic intervention in a range of diseases During this highly scientific satellite symposium, the speakers share the latest discoveries on the IL23 pathway as a therapeutic target Videos Podcasts Articles37 2695–2706 PubMed 6 Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi Establishment of a novel abdominal heart transplantation model of mice13;
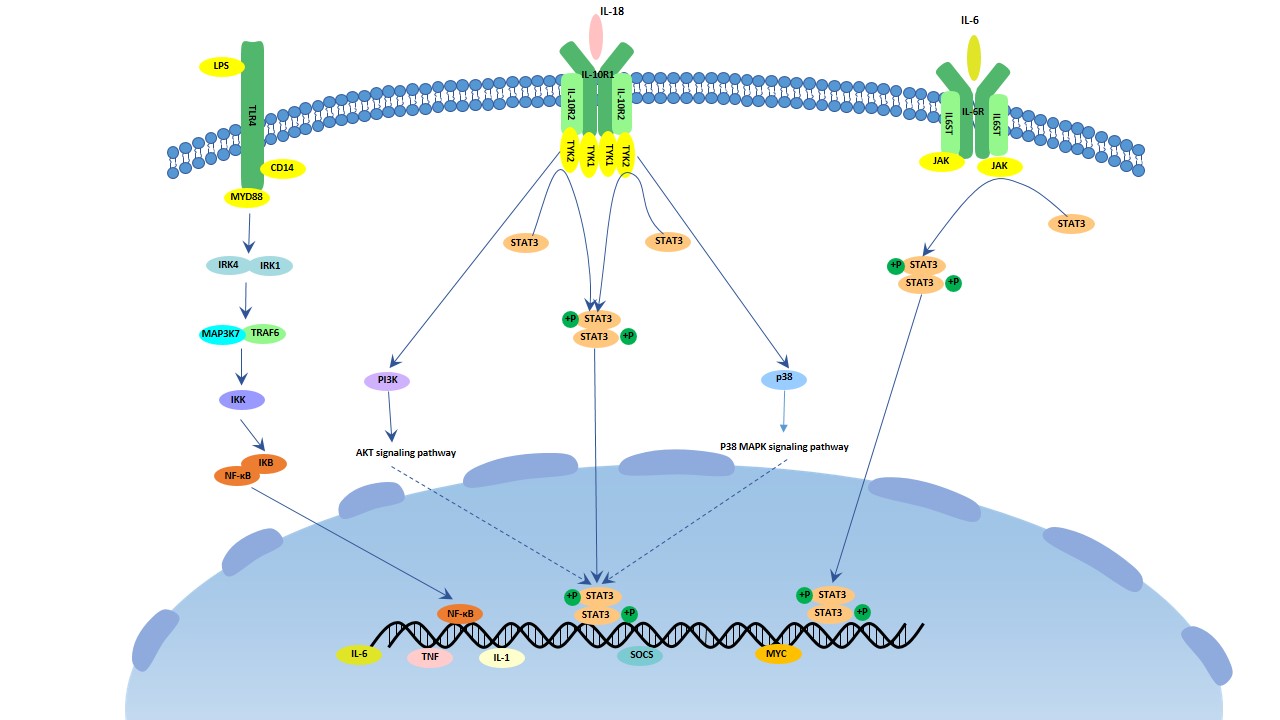


The Overview Of Interleukin


Jddonline Com Articles Dermatology Ss02x Download 1
The Translational Journey of IL23 Pathway Inhibitors in Psoriasis Professor Kenneth B Gordon There is much to be learnt from IL23 inhibitors in the treatment of psoriasis, including information about the longterm efficacy of these treatments and use in special populations, as well as information regarding treatment withdrawal andSince studies have proven that IL23 is essential for differentiation and maintenance of TH17 cells , and IL23/IL17 axis has been found to be associated with many inflammation related diseases 41–44, it can be inferred that this pathway together with other inflammation mediators such as IL1β, IL6, and TNFα may play an important roleThat's to say, high serum IL23 level and its active JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway play a critical role in resulting in high serum IL17 level and high frequency of Th17 existed in active AS patients In this way, our results suggest the possible role of JAK2/STAT3 signal pathway and IL23/Th17 axis in pathogenesis of AS



The Impact Of Genomics On Pediatric Research And Medicine American Academy Of Pediatrics



Stat3 And Nf Kb Signal Pathway Is Required For Il 23 Mediated Il 17 Production In Spontaneous Arthritis Animal Model Il 1 Receptor Antagonist Deficient Mice The Journal Of Immunology
The Interleukin 23 (IL23) cytokine is a heterodimeric cytokine consisting of the two subunits p19 and p40 It is an inducer of the Th17 cell population and a component of the IL23/IL17 immune pathway which is an orchestrator of many pathological conditions, including psoriasisThe IL23 pathway has emerged as a promising target in the management of psoriatic diseases This LIVE clinical dialogue aims to give a timely update on the newest developments from both dermatological and rheumatological perspectivesIL12, IL23 and Type I IFNs, which are critical in driving the function of Th1 cells, Th17 cells and the innate immune response8,9 Immune Cell Immune Cell Immune Cell Release of cytokines Activation of downstream signaling molecules STAT activation and relocation into the nucleus Promotes expression of e˙ector molecules Cytokines can further
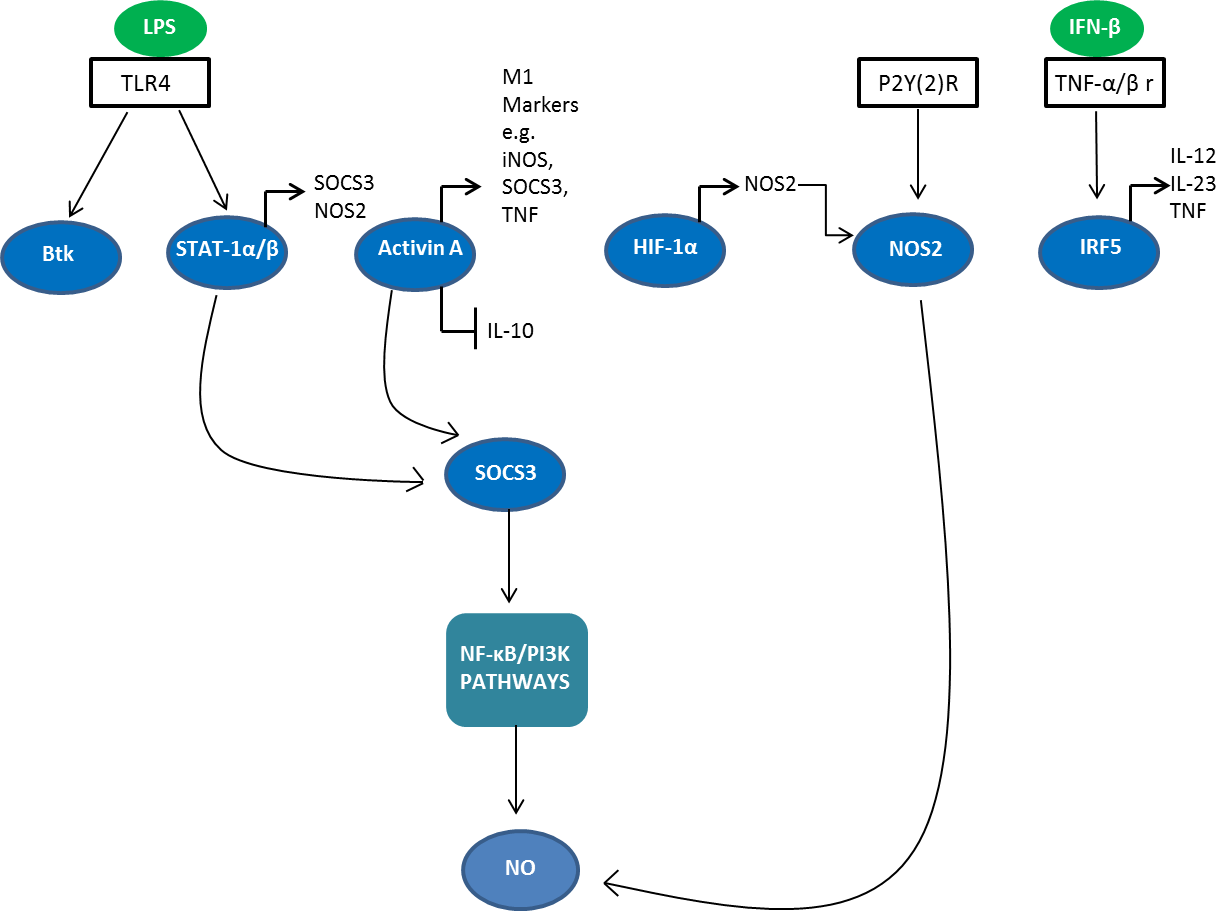


Macrophage Polarization Mini Review Bio Rad



Figure 3 From Il 12 Il 23 And Il 17 In Ibd Immunobiology And Therapeutic Targeting Semantic Scholar
IL12 Signaling Pathway Background Interleukin 12 (IL12) family is unique in having the only heterodimeric cytokines, including IL12, IL23, IL27 and IL35 The heterodimeric cytokines of the IL12 family consist of an αchain (p19, p28 or p35) and a βchain (p40 or Ebi3) The αchains have a fourhelix bundle structure characteristic ofThe crucial role of the IL23/IL17 pathway in the early recruitment of large numbers of neutrophils in mucosal and nonmucosal tissues via several cytokines and chemokines has been well documented The present study was aimed at investigating the role of the IL23/IL17 pathway in lung pathogenesis after sepsis induced by CLP using two inbred5 Zelante T, De Luca A, Bonifazi P, Montagnoli C, Bozza S, et al IL23 and the Th17 pathway promote inflammation and impair antifungal immune resistance Eur J Immunol 07;


Www Oatext Com Pdf Brcp 1 122 Pdf



Discovery Of The Il 23 Il 17 Signaling Pathway And The Treatment Of Psoriasis The Journal Of Immunology
IL23 pathway has emerged as a promising target in the management of psoriatic diseases The expert faculty provided virtual attendees with updates on the newest developments from both dermatological and rheumatological perspectives, offering invaluable insights into psoriasis and5 Zelante T, De Luca A, Bonifazi P, Montagnoli C, Bozza S, et al IL23 and the Th17 pathway promote inflammation and impair antifungal immune resistance Eur J Immunol 07;A Fresh Look at the IL23 Pathway in Psoriatic Disease Professor Kristian Reich The Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Skin Diseases Psoriasis is one of the most common inflammatory skin diseases, characterised by hyperproliferation and abnormal differentiation of epidermal keratinocytes, thereby initiating a chain of reactions resulting in skin lesions containing immune infiltrate T cells and


2
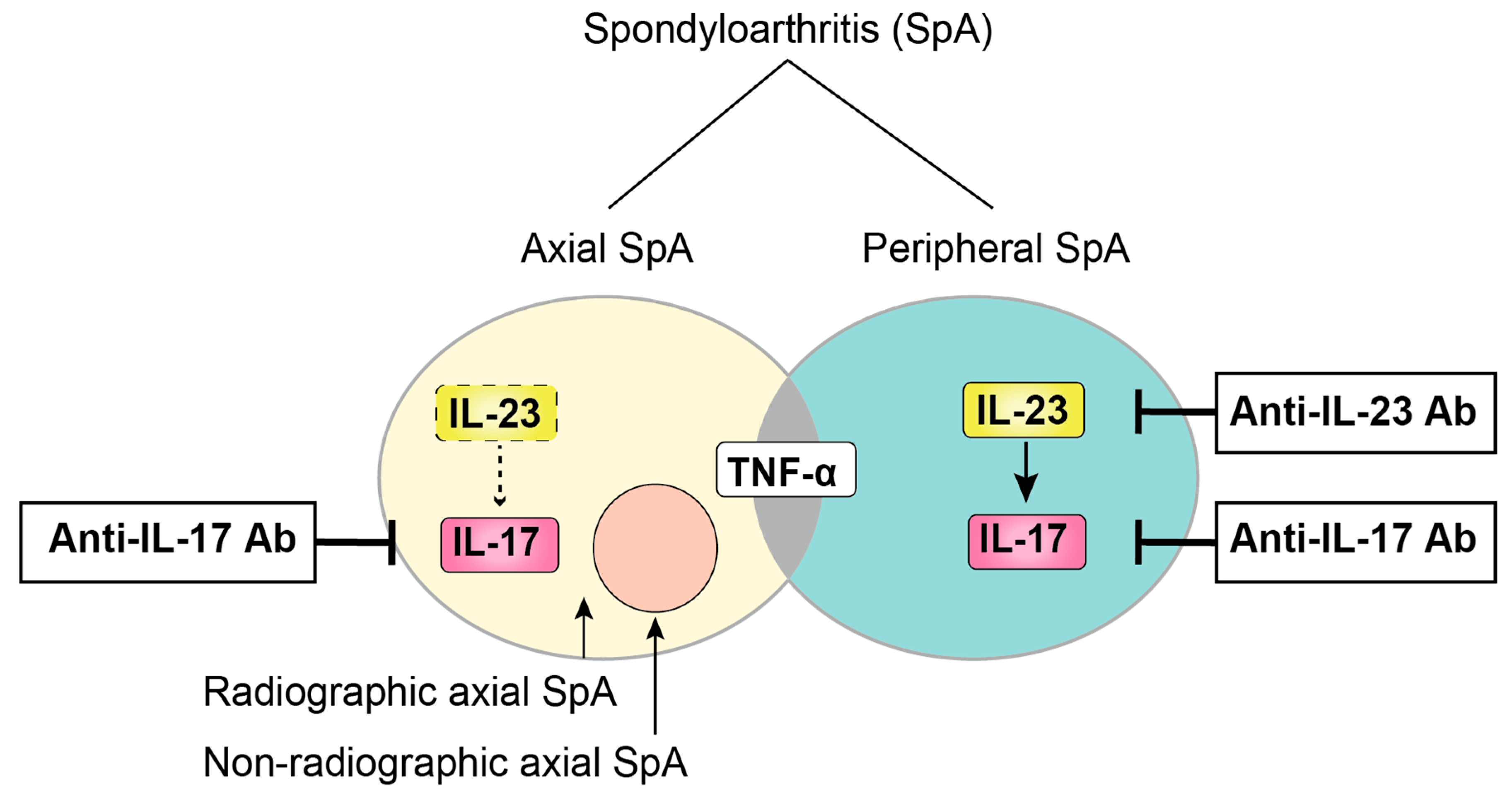


Ijms Free Full Text The Role Of The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway In The Pathogenesis Of Spondyloarthritis Html
37 2695–2706 PubMed 6 Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi Establishment of a novel abdominal heart transplantation model of mice13;Mahadevan U Targeting the IL23 Pathway Presented at Guild Conference ;The IL23/IL17 axis is an important pathway for targeted therapy for inflammatory diseases Emerging evidence from clinical trials has shown that monoclonal antibodies against IL23, IL17, and tumor necrosis factor are effective in the treatment of patients with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, hidradenitis suppurativa, pityriasis rubra pilaris


Http Website60s Com Upload Files Cytokine Vol 1 2 Pdf


Academic Oup Com Rheumatology Article Pdf 46 8 1266 Kem055 Pdf
IL23 plays a role in a signaling pathway that triggers inflammation IL23 inhibitors block the action of IL23, which can help limit the inflammation that causes psoriasis symptoms TreatmentSince studies have proven that IL23 is essential for differentiation and maintenance of TH17 cells , and IL23/IL17 axis has been found to be associated with many inflammation related diseases 41–44, it can be inferred that this pathway together with other inflammation mediators such as IL1β, IL6, and TNFα may play an important roleProf Reich discussed the role of the IL23 pathway in psoriatic skin inflammation, highlighting how IL23 inhibition results in high levels of clinical response in the majority of treated patients with psoriasis and the importance of early treatment for maximal disease modification Studies are currently ongoing



Of Inflammasomes And Alarmins Il 1b And Il 1a In Kidney Disease American Society Of Nephrology


Plos One The Role Of Il 23 Th17 Pathway In Patients With Primary Immune Thrombocytopenia
The crucial role of the IL23/IL17 pathway in the early recruitment of large numbers of neutrophils in mucosal and nonmucosal tissues via several cytokines and chemokines has been well documented The present study was aimed at investigating the role of the IL23/IL17 pathway in lung pathogenesis after sepsis induced by CLP using two inbredSpecific targeting of IL23 has already been shown in headtohead trials to have superior efficacy to ustekinumab for immunemediated conditions like psoriasis16 IL23 specific agents act through binding the p19 subunit specifically inhibiting the IL23 pathway and not the IL12 pathway



Il 32 Induced Signaling Pathways In Inflammation A During Download Scientific Diagram



Cytokines Signaling And Il17 Pathways Youtube



Il 17a Inhibition By Secukinumab Induces Early Clinical Histopathologic And Molecular Resolution Of Psoriasis Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology



A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas


Www Cell Com Immunity Pdf S1074 7613 19 1 Pdf



Il 23 Costimulates Antigen Specific Mait Cell Activation And Enables Vaccination Against Bacterial Infection Science Immunology



Il 23 Costimulates Antigen Specific Mait Cell Activation And Enables Vaccination Against Bacterial Infection Science Immunology


Signaling In The Immune Response


Mg Patients Il 23 Th17 Pathway May Be New Therapeutic Target Study Finds



Figure 1 From Interleukin 23 A New Atherosclerosis Target Semantic Scholar
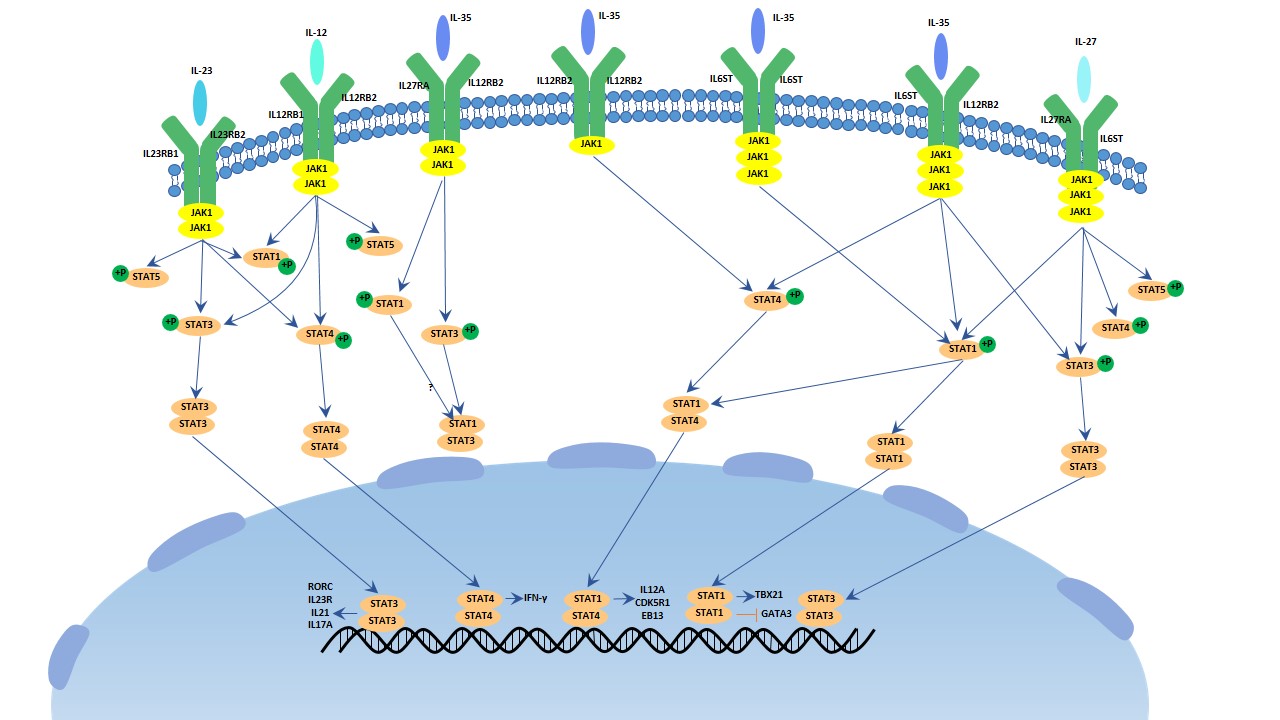


The Overview Of Interleukin


Q Tbn And9gctml7dmk4unjkgd1dfhc935 Caixjvzpfko8l6fy Usqp Cau



Stat1 Mutations In Autosomal Dominant Chronic Mucocutaneous Candidiasis Nejm
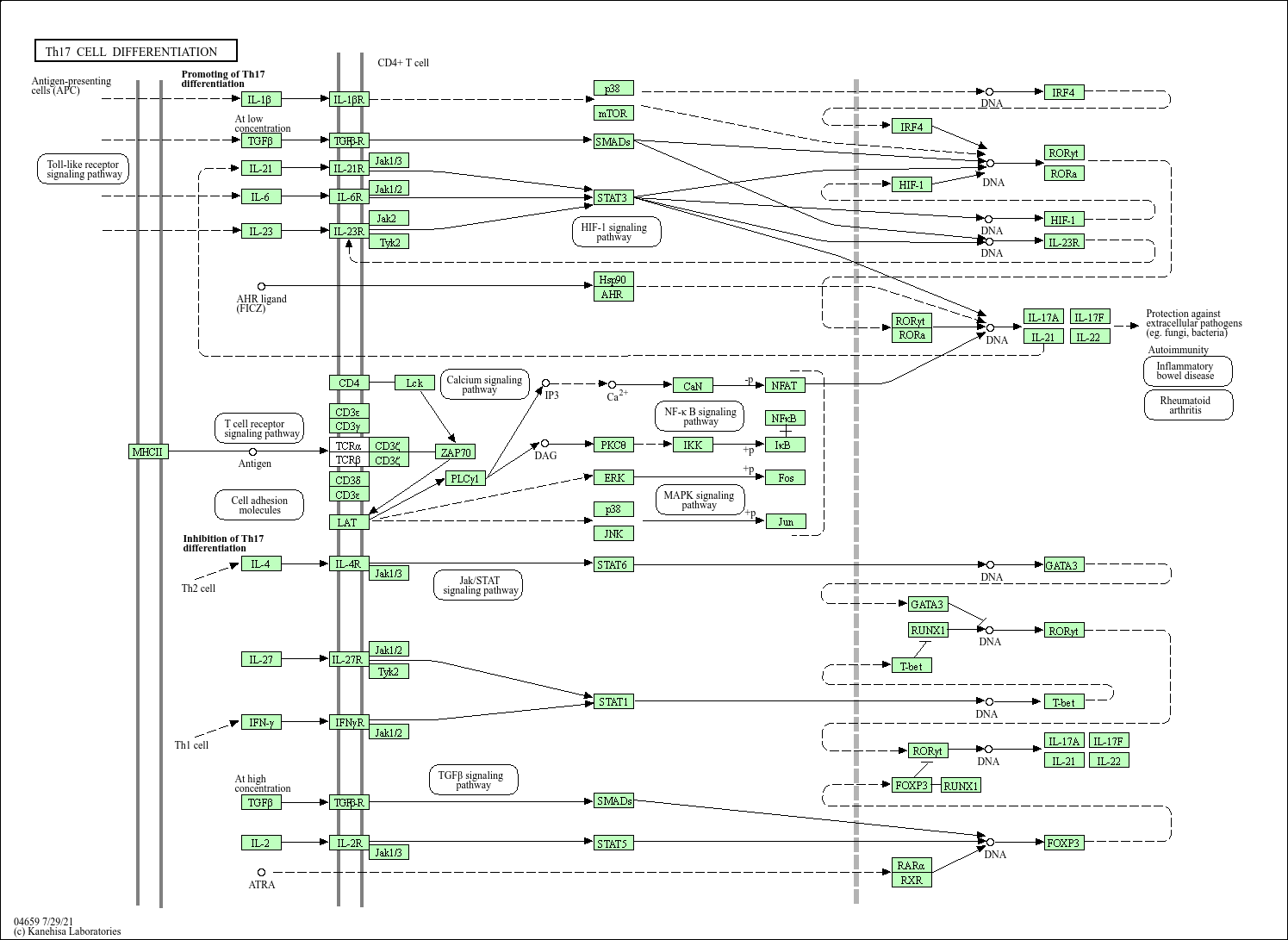


Kegg Pathway Th17 Cell Differentiation Homo Sapiens Human


Www Jaad Org Article S0190 9622 16 6 Pdf


Www Mydryeyes Org Shared Files Marketing The role of interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in mesenchymal stem cell Based tissue repair and regeneration Pdf



Il 21 Signaling In Immunity F1000research
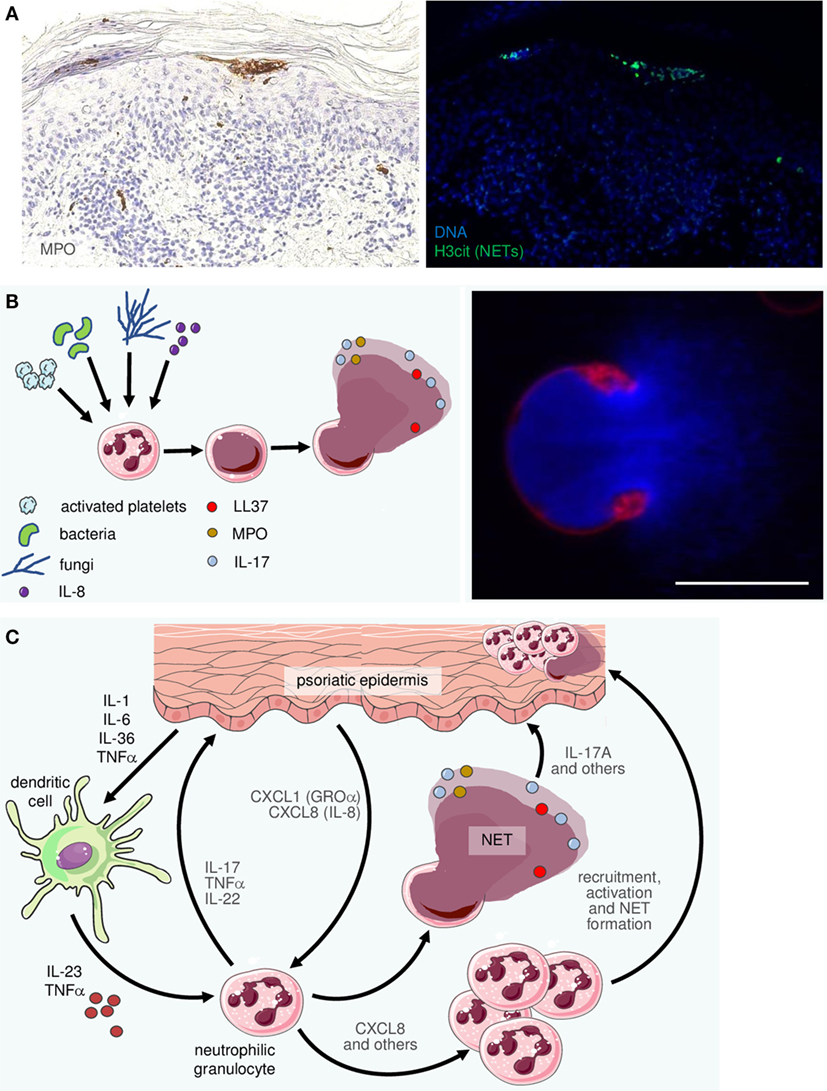


Frontiers The Interleukin 23 Interleukin 17 Axis Links Adaptive And Innate Immunity In Psoriasis Immunology



Pdf Understanding The Il 23 Il 17 Immune Pathway Semantic Scholar



Risankizumab Versus Ustekinumab For Moderate To Severe Plaque Psoriasis Nejm



Neutralization Or Absence Of The Interleukin 23 Pathway Does Not Compromise Immunity To Mycobacterial Infection Infection And Immunity



The Pathological Role Of Wnt5a In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis Tian 19 Journal Of Cellular And Molecular Medicine Wiley Online Library
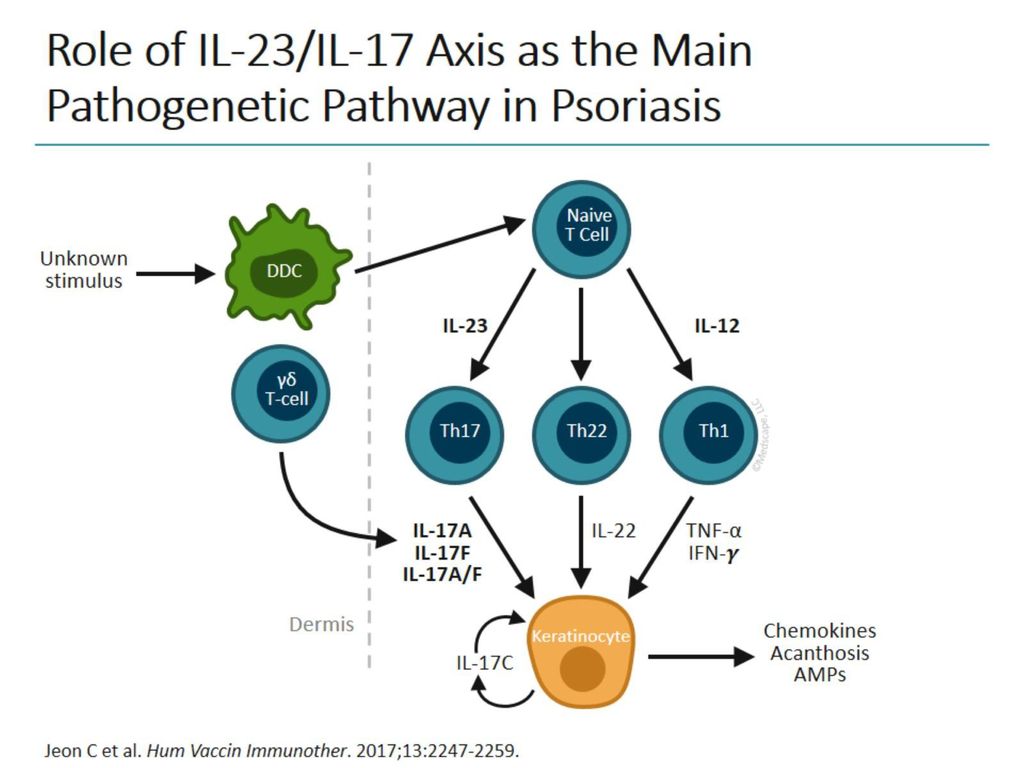


Evolution Of Treatment Strategies Targeting Il 23 For Psoriasis Ppt Download
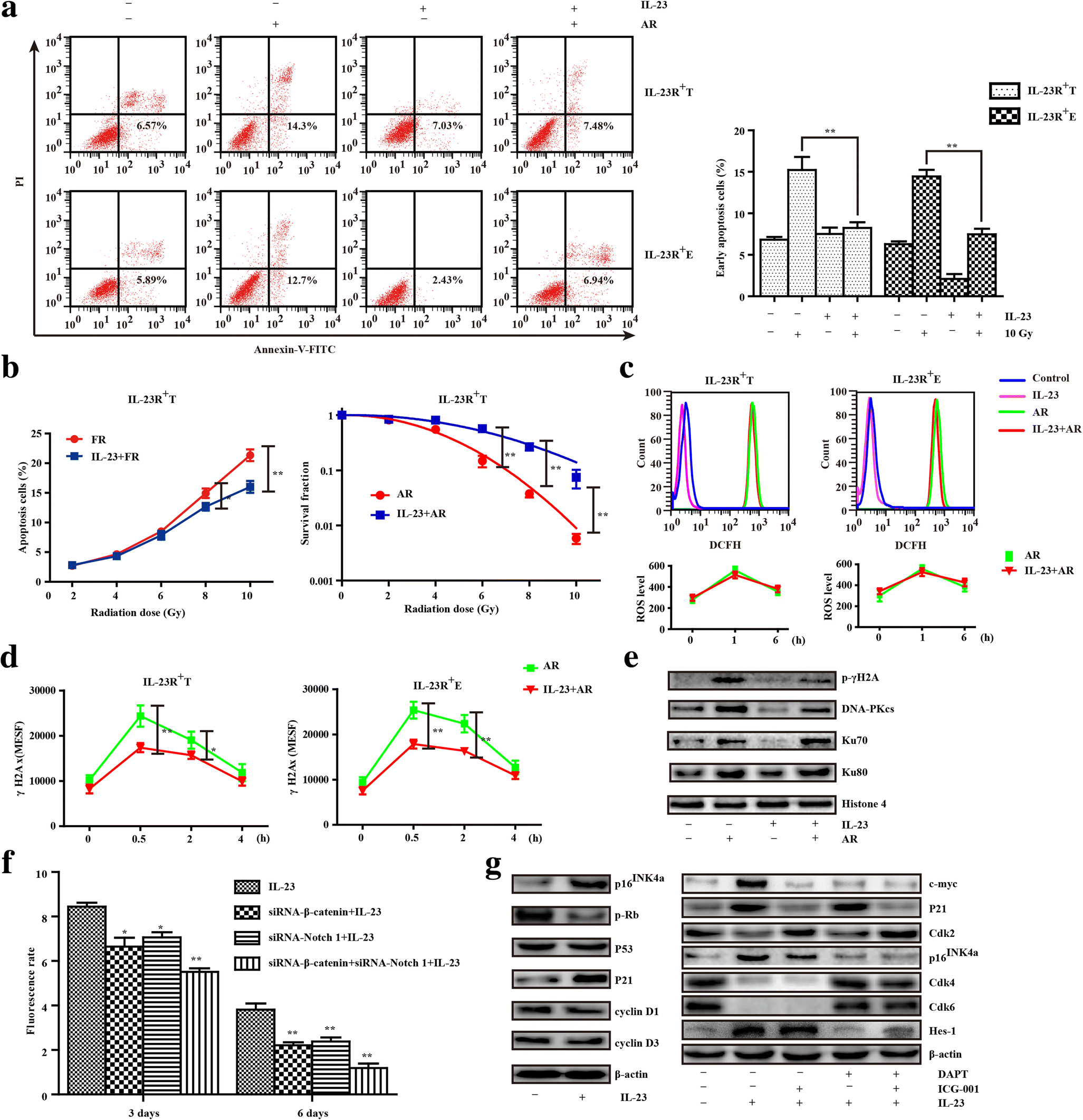


Figure 3 Interleukin 23 Receptor Signaling Mediates Cancer Dormancy And Radioresistance In Human Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma Cells Via The Wnt Notch Pathway Springerlink



New Biologic Therapies That Target The Il 12 23 Pathway Youtube
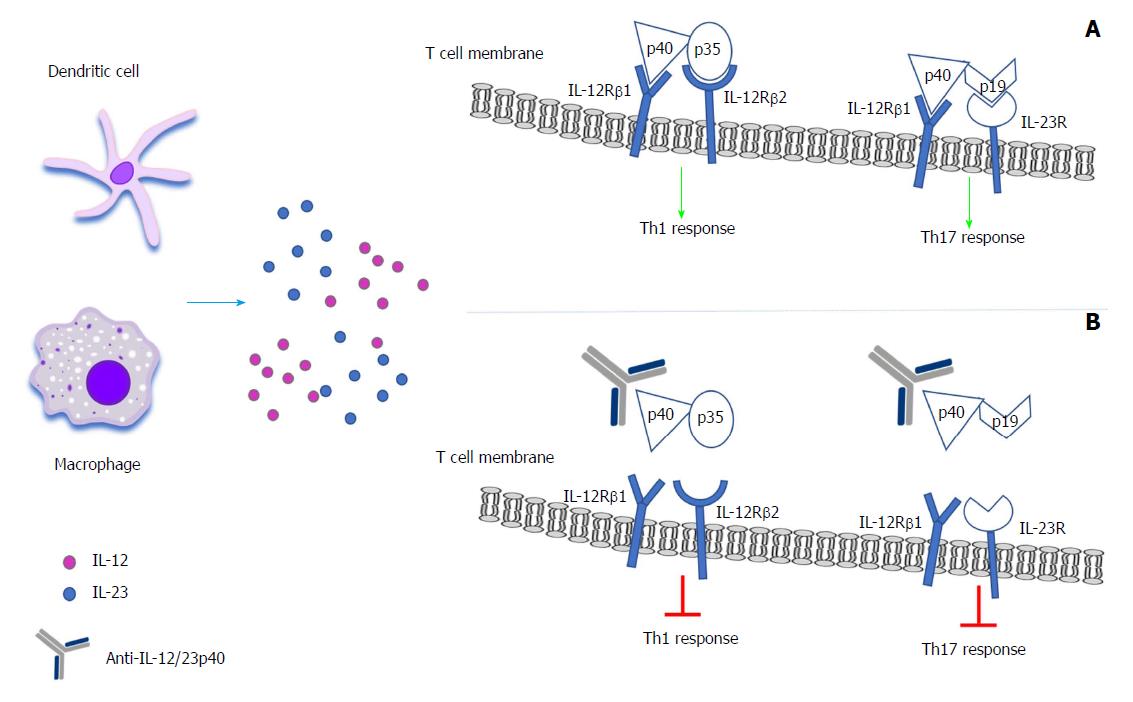


Interleukin 12 Interleukin 23 Pathway Biological Basis And Therapeutic Effect In Patients With Crohn S Disease


Q Tbn And9gcrigwlmvzgumi48 Ho Vts 9qaroas99xo1xclbyz9pq3r3tsmz Usqp Cau


Www Jci Org Articles View Version 1 Pdf Render Pdf


Www Gastrojournal Org Article S0016 5085 16 9 Pdf



Updates On Psoriasis And Cutaneous Oncology Proceedings From The 17 Mauiderm Meeting Jcad The Journal Of Clinical And Aesthetic Dermatology



A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas



Novel P19 Protein Engages Il 12p40 To Form A Cytokine Il 23 With Biological Activities Similar As Well As Distinct From Il 12 Sciencedirect


Assessing The Relative Efficacy Of Interleukin 17 And Interleukin 23 Targeted Treatments For Moderate To Severe Plaque Psoriasis A Systematic Review And Network Meta Analysis Of Pasi Response



Therapeutic Blockade Of Granulocyte Macrophage Colony Stimulating Factor In Covid 19 Associated Hyperinflammation Challenges And Opportunities The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
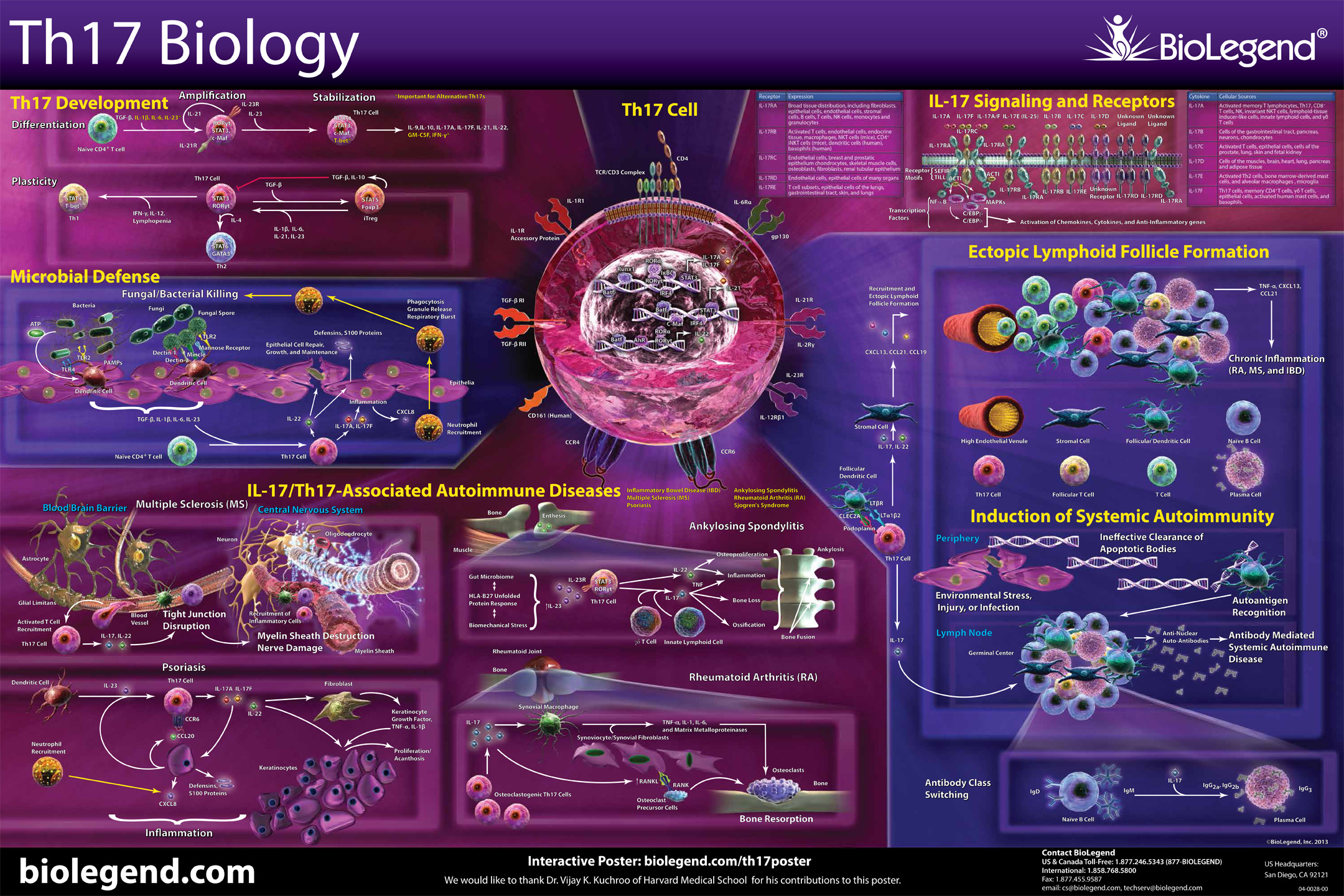


Th17 Biology


Www Jacionline Org Article S0091 6749 17 1 Pdf



Onlineseminar Webinar Evolving Insights In The Il 23 Path



Il 22 There Is A Gap In Our Knowledge Immunohorizons



Ectopic Lymphoid Neogenesis Is Strongly Associated With Activation Of The Il 23 Pathway In Rheumatoid Synovitis Topic Of Research Paper In Clinical Medicine Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On



Dithranol Targets Keratinocytes Their Crosstalk With Neutrophils And Inhibits The Il 36 Inflammatory Loop In Psoriasis Elife



Th17 Differentiation Interactive Pathway R D Systems
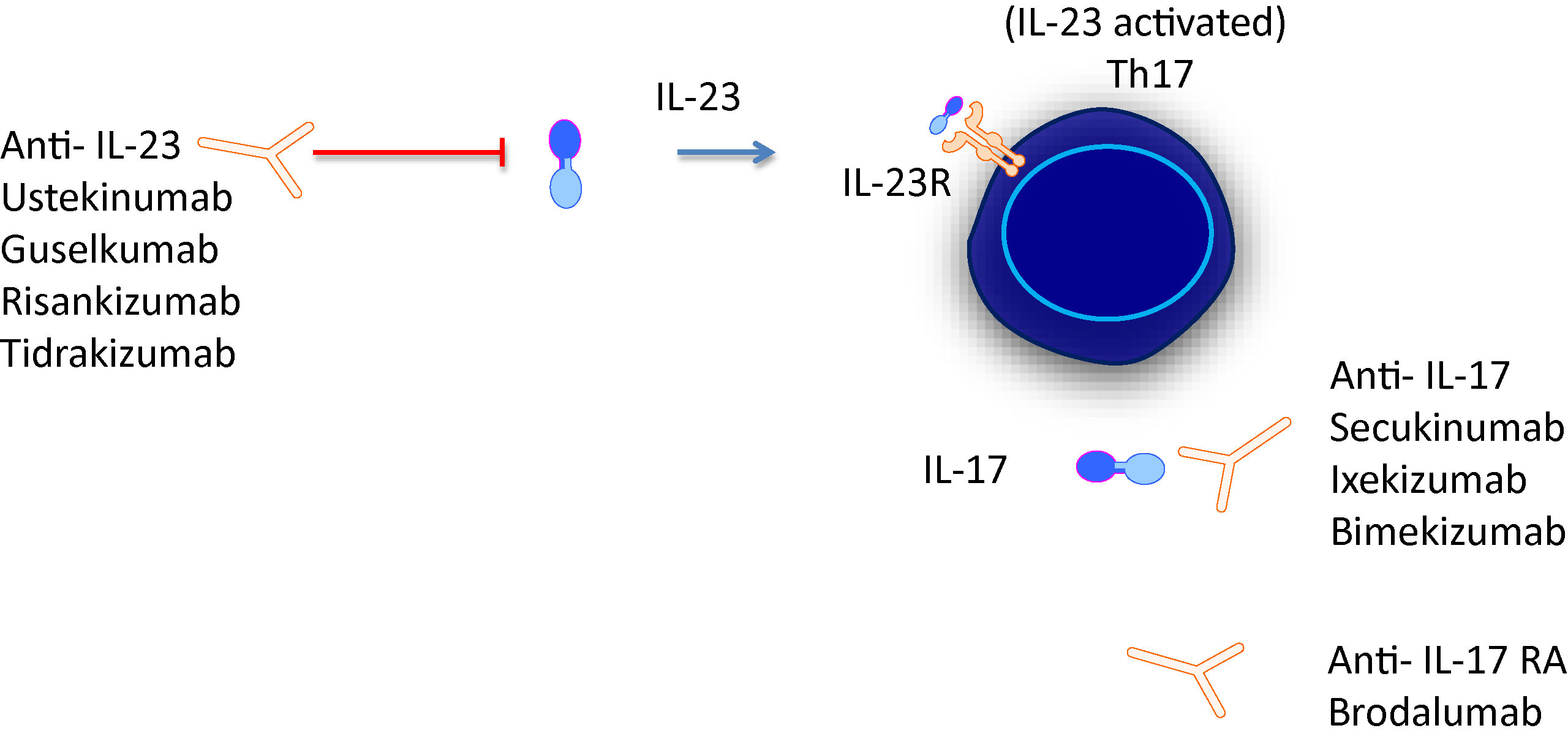


Frontiers Mini Review New Treatments In Psoriatic Arthritis Focus On The Il 23 17 Axis Pharmacology


Digitalcommons Wustl Edu Cgi Viewcontent Cgi Article 6660 Context Open Access Pubs



Pathways Abcepta



Biomarkers Of Therapeutic Response In The Il 23 Pathway In Inflammatory Bowel Disease Topic Of Research Paper In Clinical Medicine Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science



The Role Of Il 17a In Axial Spondyloarthritis And Psoriatic Arthritis Recent Advances And Controversies Annals Of The Rheumatic Diseases



Il 17 And Th17 Cells In Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis And Vascular Biology
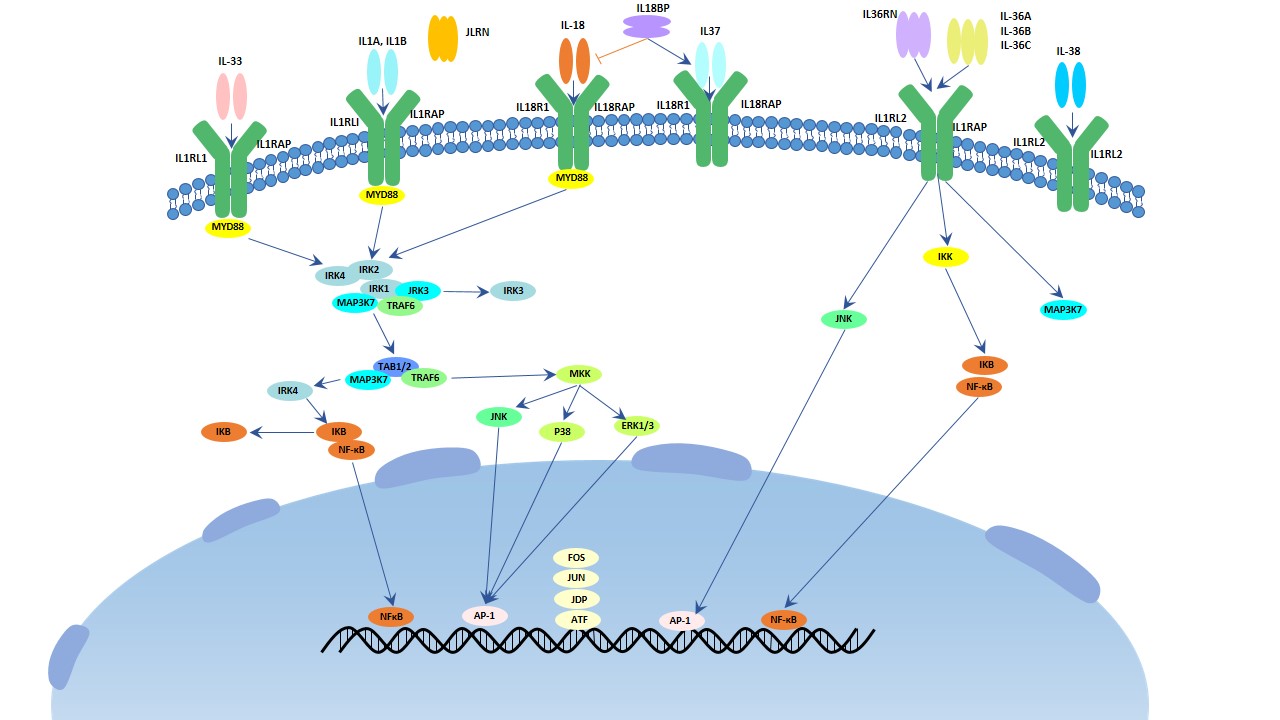


The Overview Of Interleukin


Il 23 Signaling Regulation Of Pro Inflammatory T Cell Migration Uncovered By Phosphoproteomics



Il 36 Signaling Facilitates Activation Of The Nlrp3 Inflammasome And Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Renal Inflammation And Fibrosis American Society Of Nephrology


Http Jpad Com Pk Index Php Jpad Article Viewfile 1017 944


Q Tbn And9gcs0ve3qqqaeeohg8ilakgxhzdt 2ghrznrijgfhunz Kagtpgkv Usqp Cau



Il 23 Mobilizes The Endogenous Pge 2 Ep2 Ep4 Camp Pka Pathway To Download Scientific Diagram


Bmcrheumatol Biomedcentral Com Track Pdf 10 1186 S 017 0004 5



Psoriasis Translating Current And Emerging Therapies Into Enhanced Management Strategies Youtube
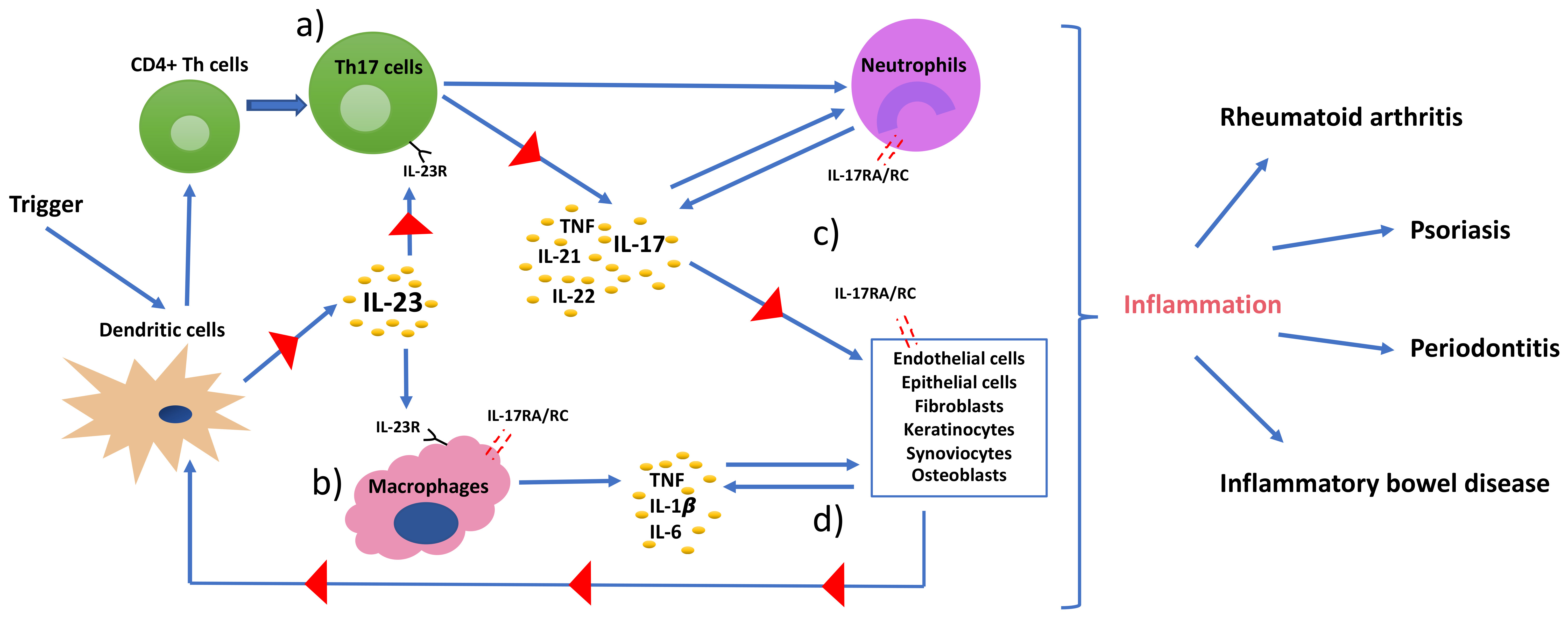


Ijms Free Full Text Th17 Cells And The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In The Pathogenesis Of Periodontitis And Immune Mediated Inflammatory Diseases Html
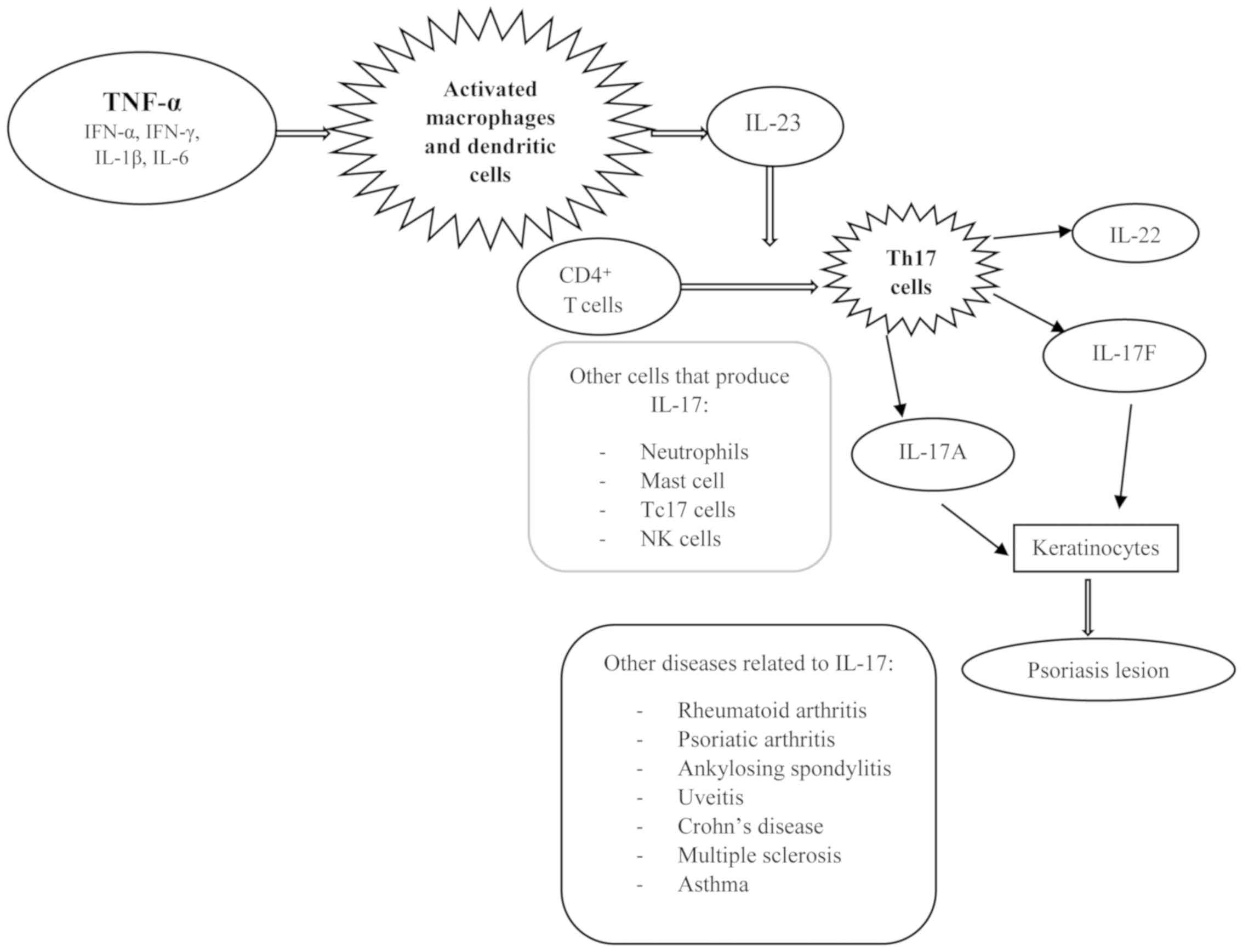


Psoriasis Association Of Interleukin 17 Gene Polymorphisms With Severity And Response To Treatment Review
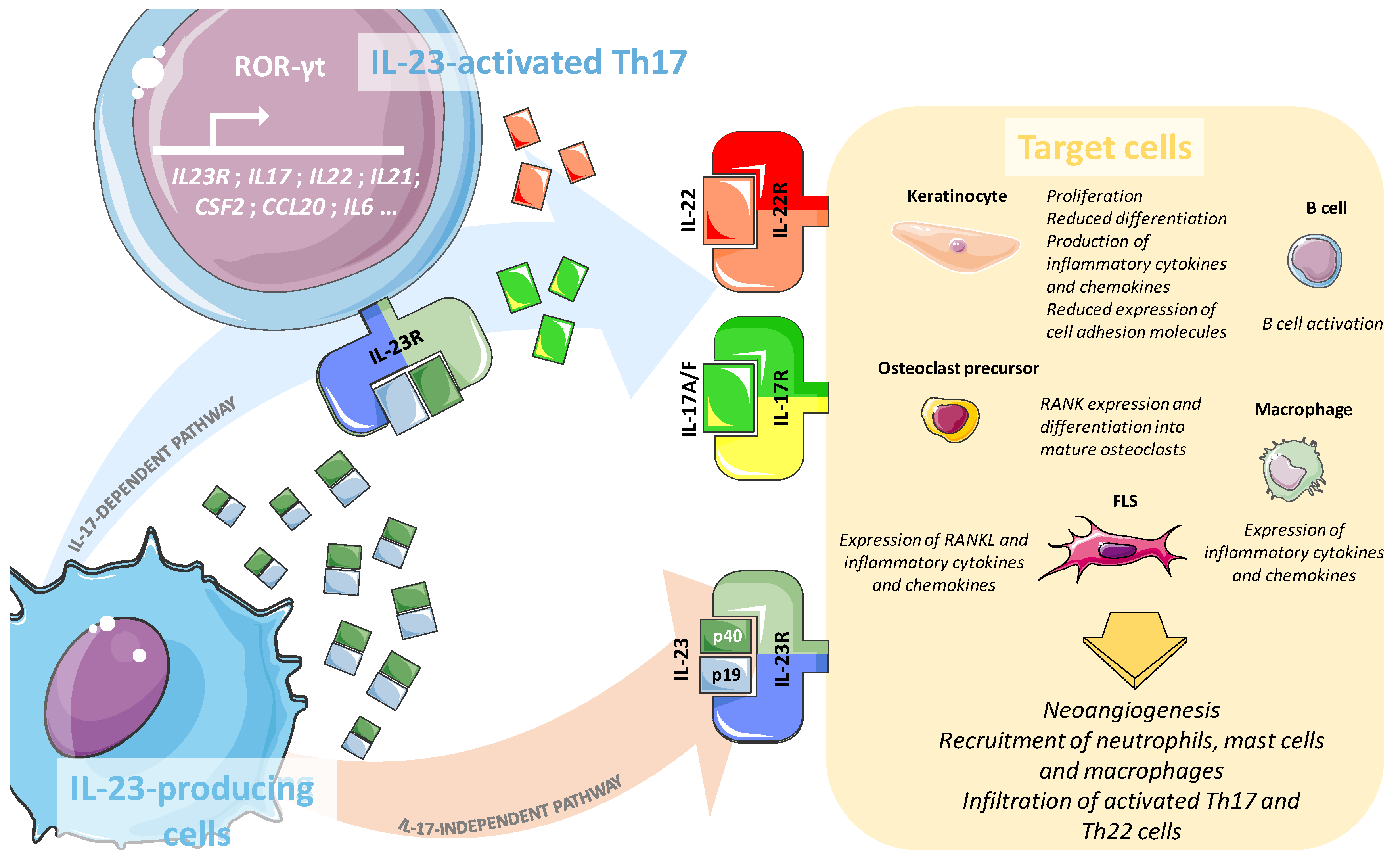


Ijms Free Full Text Role Of The Il 23 Il 17 Axis In Psoriasis And Psoriatic Arthritis The Clinical Importance Of Its Divergence In Skin And Joints Html
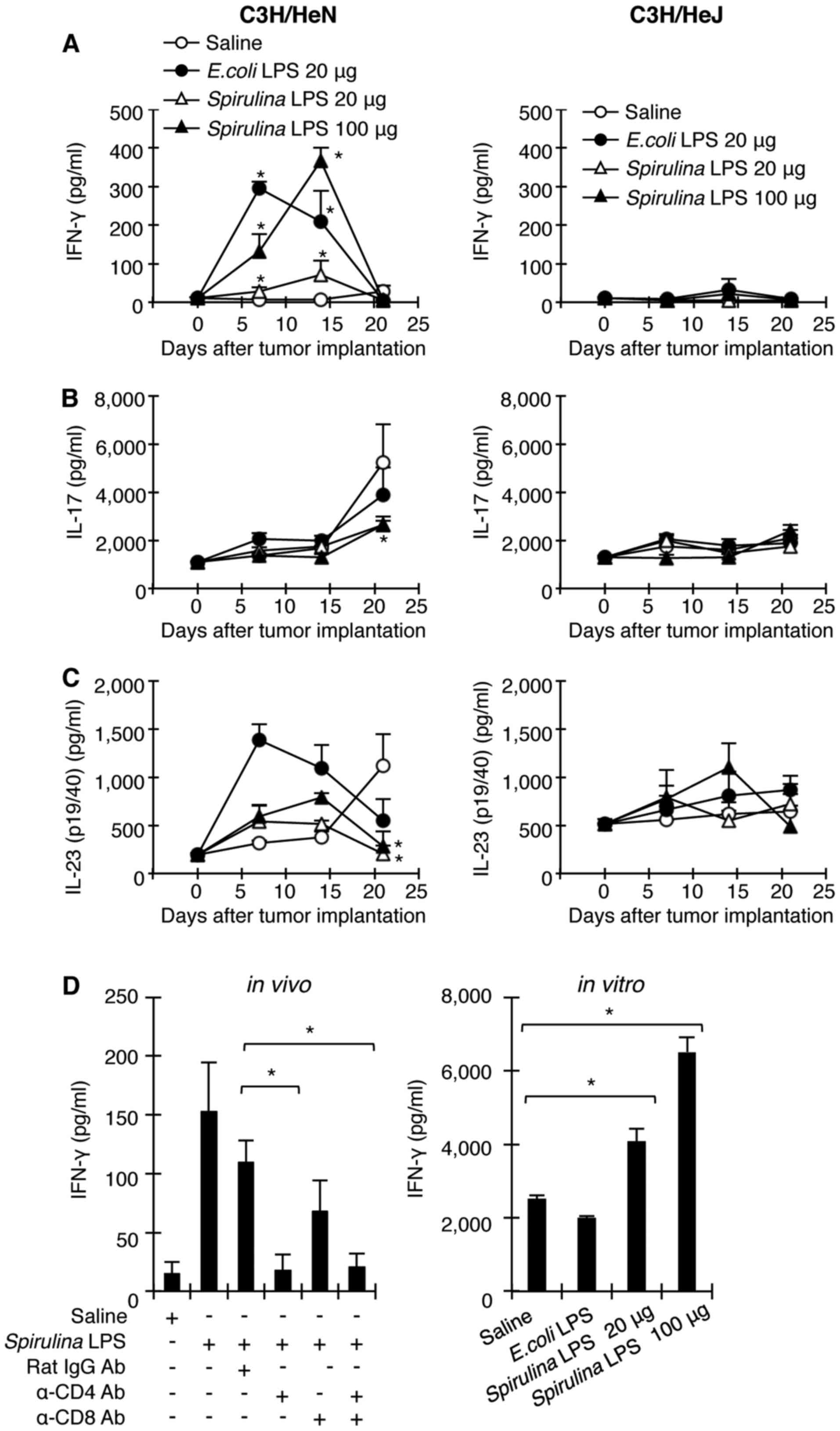


Spirulina Lipopolysaccharides Inhibit Tumor Growth In A Toll Like Receptor 4 Dependent Manner By Altering The Cytokine Milieu From Interleukin 17 Interleukin 23 To Interferon G
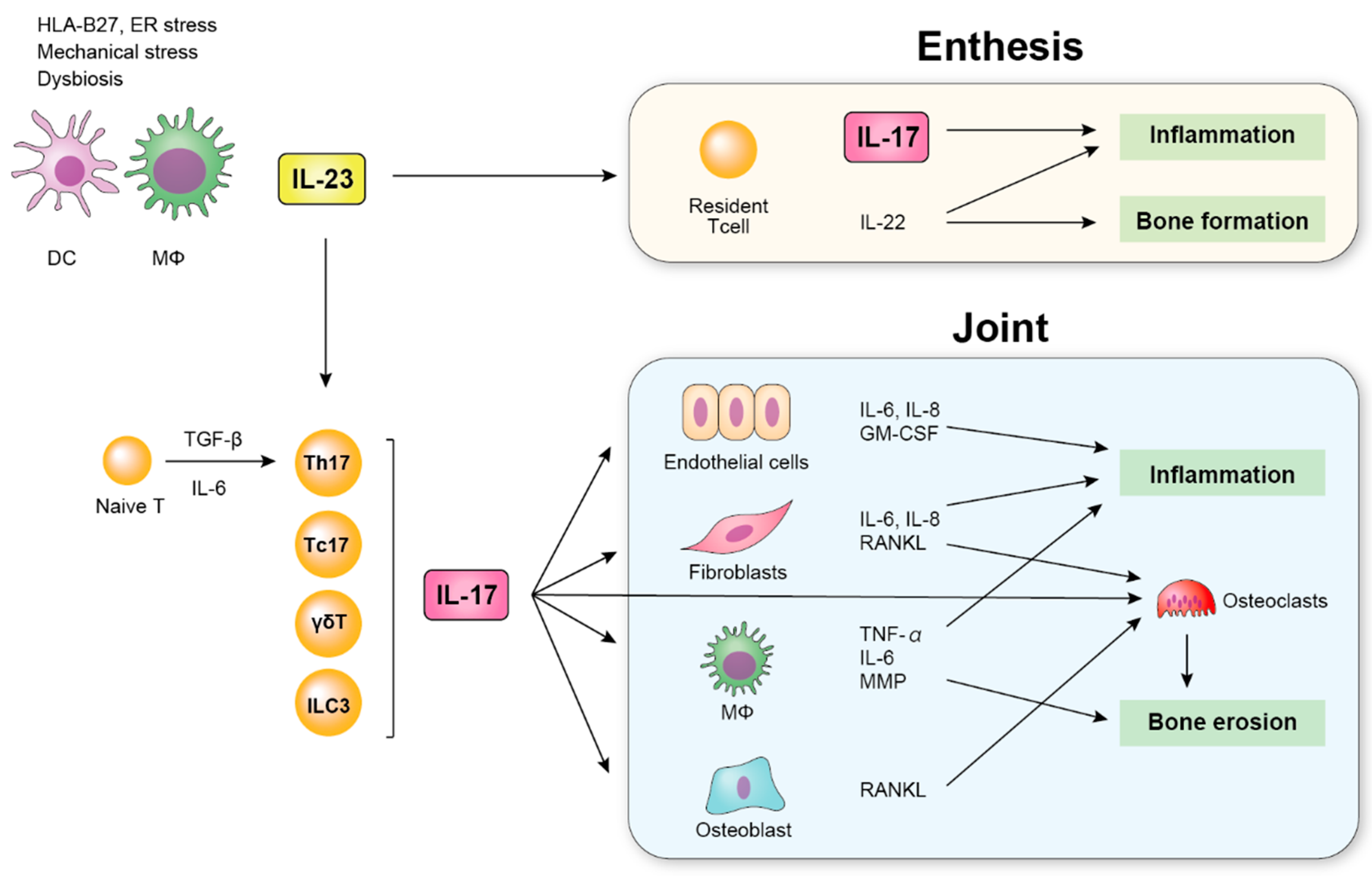


Ijms Free Full Text The Role Of The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway In The Pathogenesis Of Spondyloarthritis Html



Natrevrheumatol New Review Now Online The Il 23 Il 17 Pathway As A Therapeutic Target In Axial Spondyloarthritis Therapy Spondyloarthritis Axialspa Immunopathogenesis Check It Out At T Co Dabfrsmq1e T Co Ggjnf3knzq


Q Tbn And9gctknda Sihqkqm Fisk5pqk4a5nb Irkeweixmpoesa8 Yqxxu Usqp Cau



The Role Of Il 23 And The Il 23 Th17 Immune Axis In The Pathogenesis And Treatment Of Psoriasis Girolomoni 17 Journal Of The European Academy Of Dermatology And Venereology Wiley Online Library


Rupress Org Jem Article Pdf 4 13 31 Jem Pdf


Www Cell Com Cell Reports Pdf S2211 1247 18 0 Pdf



Putting Together The Psoriasis Puzzle An Update On Developing Targeted Therapies Disease Models Mechanisms
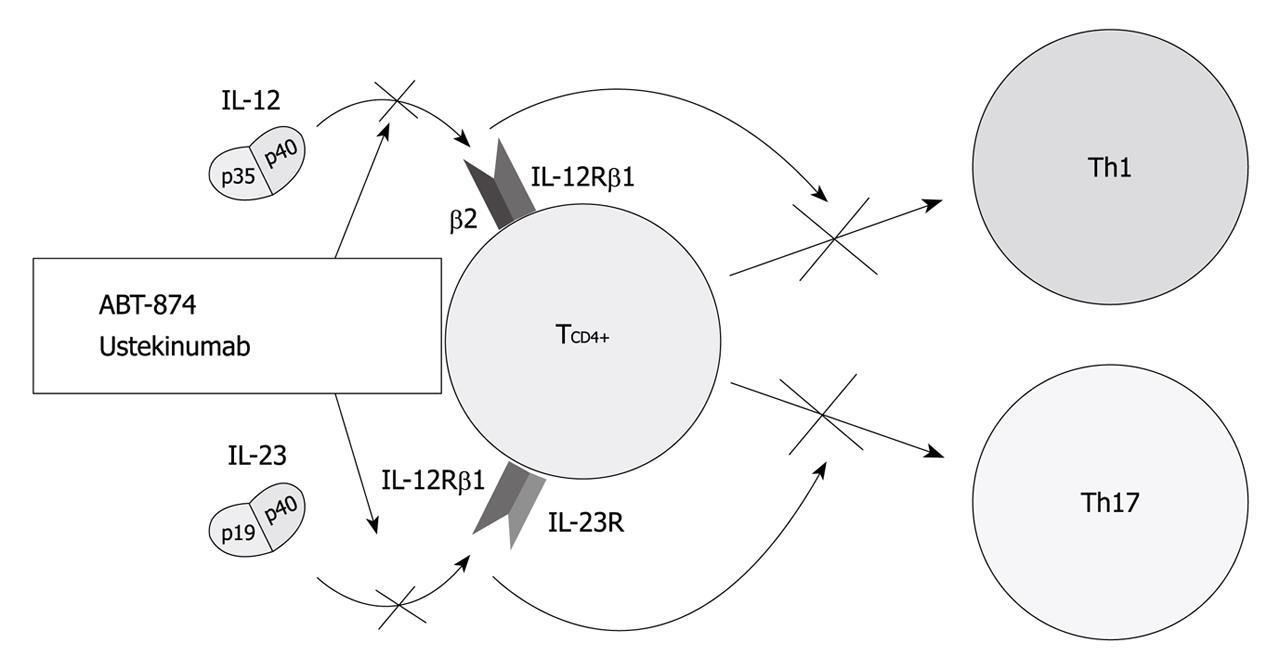


Recent Advances In Cytokines Therapeutic Implications For Inflammatory Bowel Diseases



A Cytokine Network Involving Il 36g Il 23 And Il 22 Promotes Antimicrobial Defense And Recovery From Intestinal Barrier Damage Pnas



Metabolic And Epigenomic Regulation Of Th17 Treg Balance By The Polyamine Pathway Biorxiv
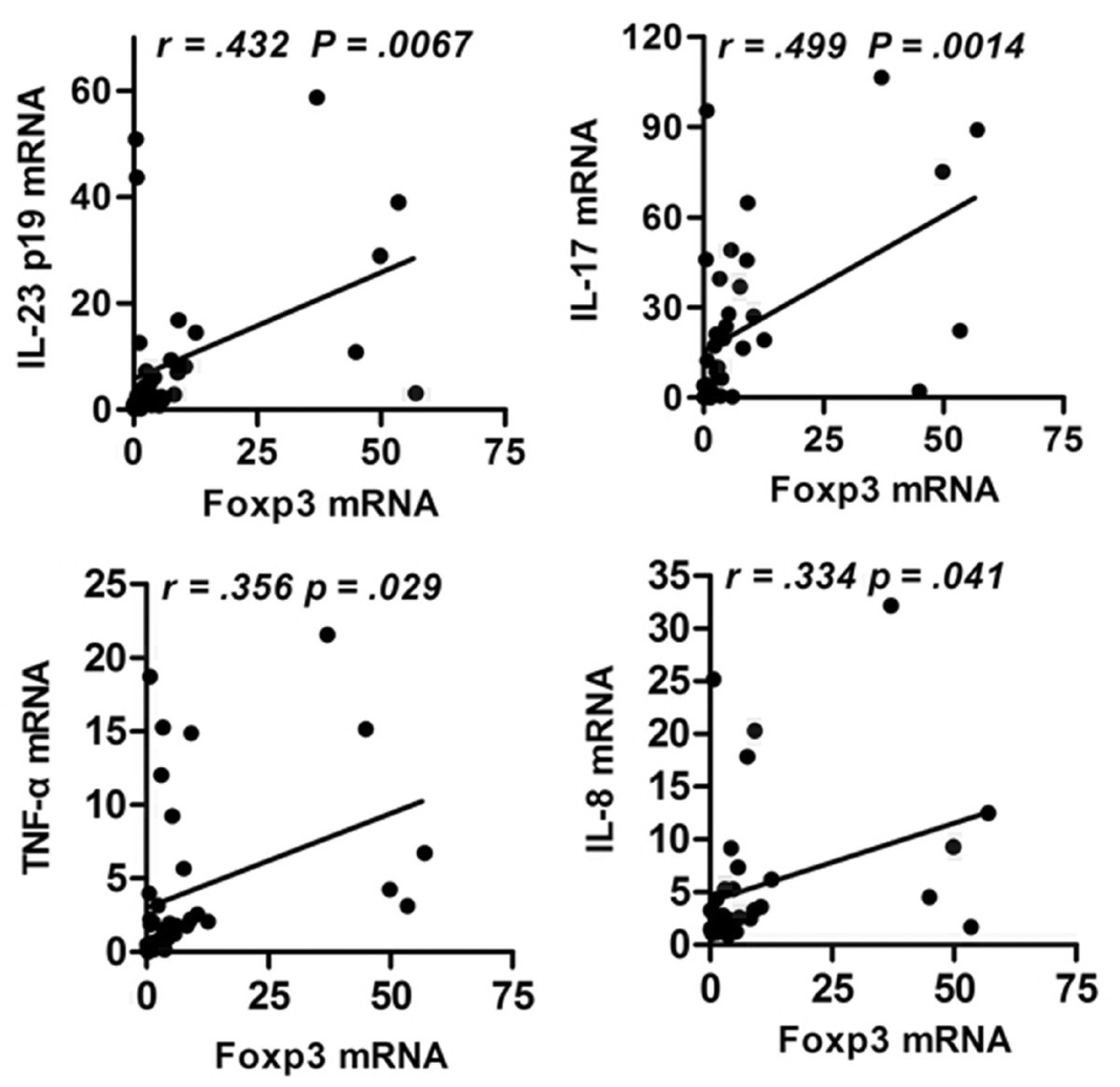


Activated Il 23 Il 17 Pathway Closely Correlates With Increased Foxp3 Expression In Livers Of Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Bmc Immunology Full Text



No comments:
Post a Comment